The Multimodal Layout Builder feature in the recipes enables users to easily create, customize, and manage evaluation forms for GenAI use cases via GenAI Evaluation Studio.
At its core, a Multimodal Recipe is a JSON configuration that defines:
The structure and layout of the form.
The fields and components displayed.
The user interaction experience.
The validation and logic applied to the form data.
Dataloop’s Multimodal Recipe provides a streamlined and adaptable framework for evaluating GenAI models across various output types, including text, multimodal, and conversational formats. Users can jumpstart their evaluation process with pre-built templates tailored for common use cases, or craft fully customized evaluation interfaces using JSON editing.
Multimodal Recipe (JSON)
The Multimodal Recipe is the foundational element of Dataloop’s GenAI Evaluation Studio, defined through a fully configurable JSON structure. Designed for flexibility, it enables users to construct complex GenAI evaluation workflows via configuration—without requiring extensive coding.
Recipe Structure
A Multimodal Recipe (written in JSON format) describes:
Sections: Logical groupings of form elements (similar to tabs or blocks), organizing the form into manageable parts.
Layout Direction: Defines the arrangement of components within sections — either horizontal or vertical.
Components: The actual interactive elements used in the form, such as text inputs, sliders, file uploads, ratings, conversations, media viewers (image, audio, video, markdown, external URLs), and more.
Logic: Rules for conditional visibility, dynamic behavior, hierarchical dependencies, and validation logic.
Styling: Custom CSS definitions that control the visual appearance of the form and its components.
Behavior: Custom JavaScript modules that introduce advanced interactivity, dynamic validations, and real-time form manipulation.
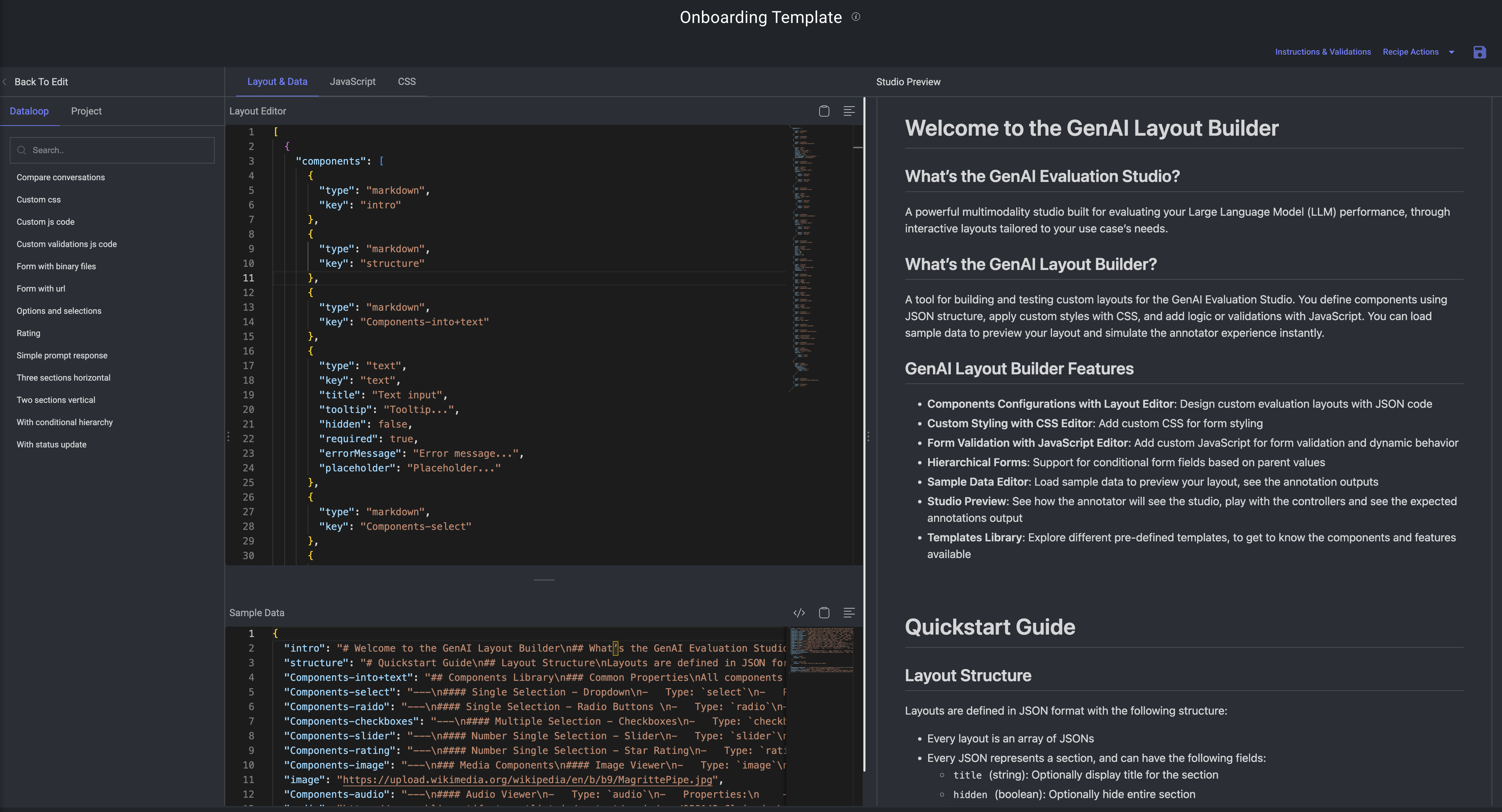
A recipe template has the following sections:
Layout Editor
The Layout Editor is a critical tool in the recipe creation process. It lets you design and control the structure of the evaluation form used by annotators in the studio. You can:
Customize your own layout using JSON schema.
Choose from a variety of UI components such as:
select– dropdownstext– text inputs or promptsradio– radio buttons for single-choice selectioncheckbox,slider, etc.
Define base properties like
label,values,default value,tooltips, andplaceholder.
For example,
[
{
"components": [
{
"type": "markdown",
"key": "intro"
},
{
"type": "markdown",
"key": "structure"
},
{
"type": "markdown",
"key": "Components-into+text"
},
{
"type": "text",
"key": "text",
"title": "Text input",
"tooltip": "Tooltip...",
"hidden": false,
"required": true,
"errorMessage": "Error message...",
"placeholder": "Placeholder..."
},
{
"type": "markdown",
"key": "Components-select"
},
{
"type": "select",
"key": "select",
"title": "Dropdown input",
"options": [
{
"label": "Option1",
"value": "Value1"
},
{
"label": "Option2",
"value": "Value2"
}
]
},
{
"type": "markdown",
"key": "Components-raido"
},
{
"type": "radio",
"key": "radio",
"title": "Radio input",
"options": [
{
"label": "Option1",
"value": "Value1"
},
{
"label": "Option2",
"value": "Value2"
}
]
},
{
"type": "markdown",
"key": "Components-checkboxes"
},
{
"type": "checkbox",
"key": "checkbox",
"title": "Checkbox input",
"options": [
{
"label": "Option1",
"value": "Value1"
},
{
"label": "Option2",
"value": "Value2"
}
]
},
{
"type": "markdown",
"key": "Components-slider"
},
{
"type": "slider",
"key": "slider",
"title": "Slider input",
"min": 0,
"max": 100,
"step": 1,
"default": 50
},
{
"type": "markdown",
"key": "Components-rating"
},
{
"type": "rating",
"key": "rating",
"title": "Star-rating input",
"maxStars": 5,
"showValue": true
},
{
"type": "markdown",
"key": "Components-image"
},
{
"type": "image",
"key": "image",
"title": "Image viewer"
},
{
"type": "markdown",
"key": "Components-audio"
},
{
"type": "audio",
"key": "audio",
"title": "Audio player"
},
{
"type": "markdown",
"key": "Components-video"
},
{
"type": "video",
"key": "video",
"title": "Video player"
},
{
"type": "markdown",
"key": "Components-url"
},
{
"type": "url",
"key": "url",
"title": "URL viewer"
},
{
"type": "markdown",
"key": "Components-markdown"
},
{
"type": "markdown",
"key": "Components-conversation"
},
{
"type": "conversation",
"key": "conversation",
"title": "Conversation viewer"
},
{
"type": "markdown",
"key": "Components-condition"
},
{
"type": "radio",
"key": "parentField",
"title": "Click to show",
"options": [
{
"label": "Show",
"value": "true"
}
]
},
{
"type": "image",
"key": "childField",
"hierarchy": {
"condition": {
"parentField": {
"$eq": "true"
}
}
}
},
{
"type": "markdown",
"key": "Components-more-conditions"
},
{
"type": "markdown",
"key": "js-css"
}
]
}
]Sample Data
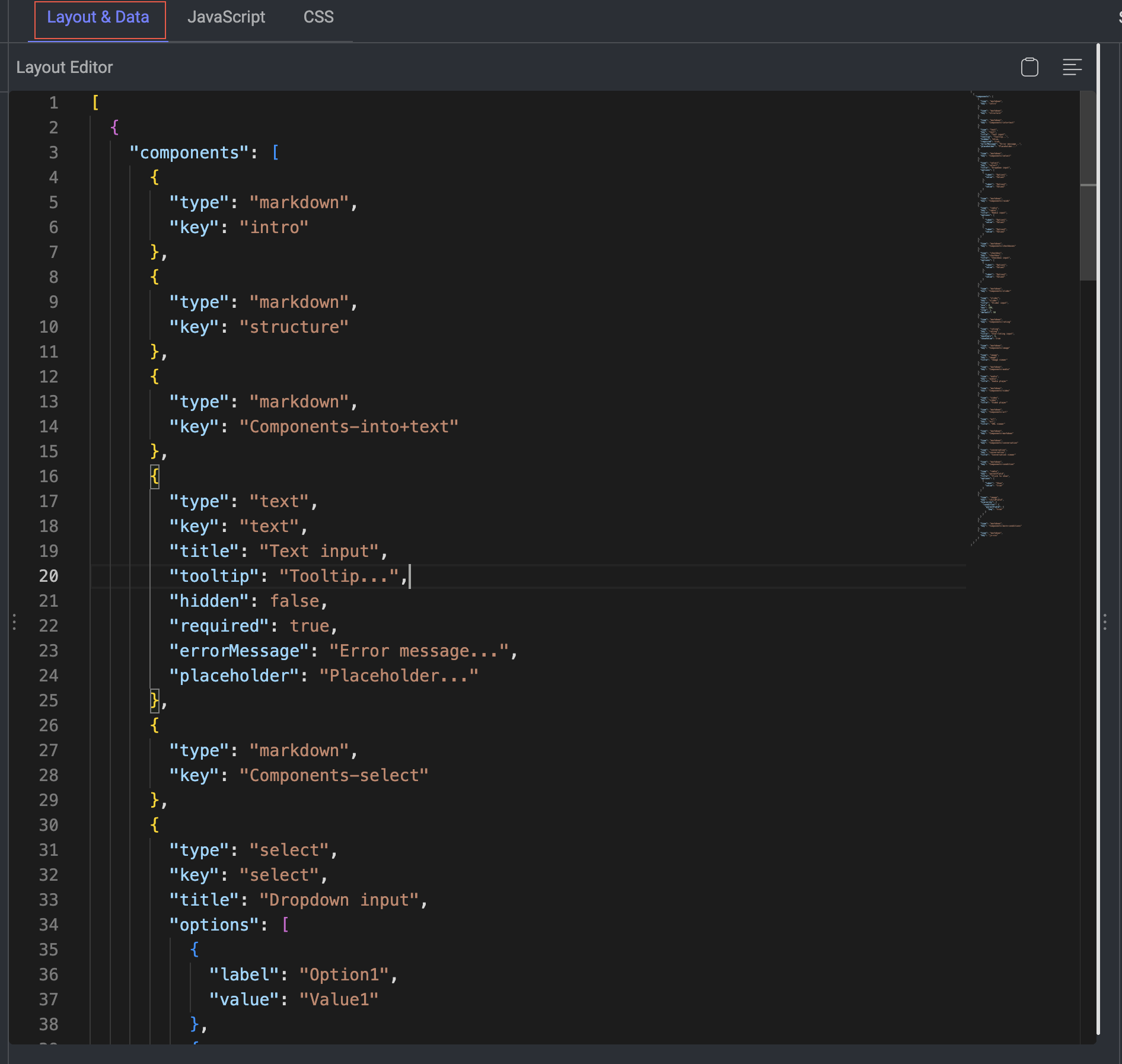
In the GenAI Multimodal Recipe of the Dataloop platform, the Sample Data section plays an essential role in the design and testing process for annotation workflows—especially within the GenAI Evaluation Studio. It allows you to populate placeholders in your Layout Editor with sample inputs. It also displays a sample of the annotation output after interacting with the Studio preview. Dataloop highly recommends exploring the preview yourself to better understand how the configuration behaves and how the outputs are generated.
The Sample Data section is designed to simulate or preview how a layout will behave before integrating real data or running actual annotations. It allows developers, annotation leads, and evaluators to:
Populate the layout with mock inputs.
Validate the design, spacing, logic, and visibility conditions in the Studio Preview.
Test dynamic elements like JavaScript validation or conditional formatting in the Studio Preview.
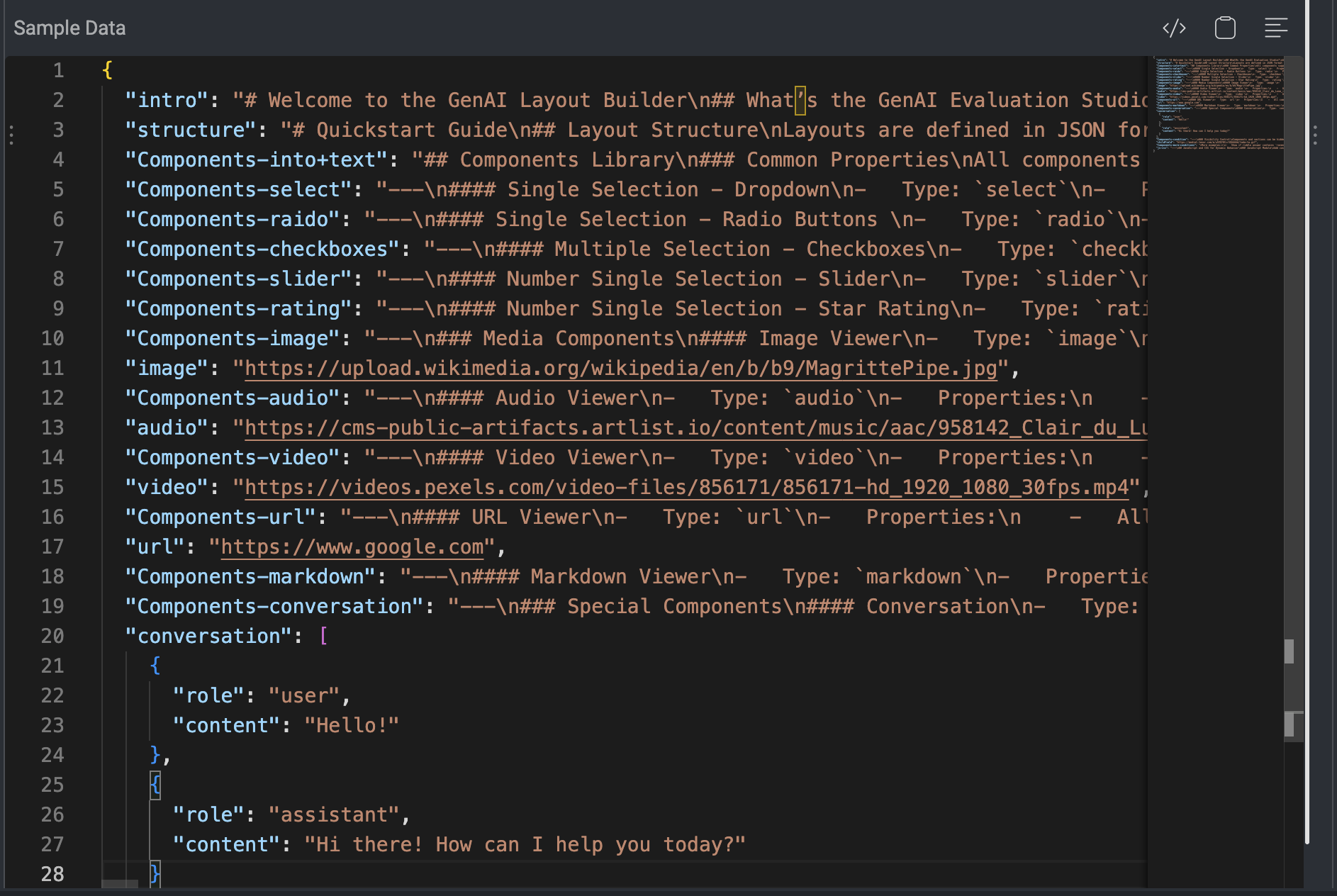
The following JSON snippet defines separate chat histories: . These are matched to UI components (e.g., two chat boxes) created in the Layout Editor.
{
"intro": "# Welcome to the GenAI Layout Builder\n## What’s the GenAI Evaluation Studio?\nA powerful Multimodal studio built for evaluating your Large Language Model (LLM) performance, through interactive layouts tailored to your use case’s needs. \n## What’s the GenAI Layout Builder?\nA tool for building and testing custom layouts for the GenAI Evaluation Studio. You define components using JSON structure, apply custom styles with CSS, and add logic or validations with JavaScript. You can load sample data to preview your layout and simulate the annotator experience instantly.\n## GenAI Layout Builder Features\n- **Components Configurations with Layout Editor**: Design custom evaluation layouts with JSON code\n- **Custom Styling with CSS Editor**: Add custom CSS for form styling\n- **Form Validation with JavaScript Editor**: Add custom JavaScript for form validation and dynamic behavior\n- **Hierarchical Forms**: Support for conditional form fields based on parent values\n- **Sample Data Editor**: Load sample data to preview your layout, see the annotation outputs\n- **Studio Preview**: See how the annotator will see the studio, play with the controllers and see the expected annotations output\n- **Templates Library**: Explore different pre-defined templates, to get to know the components and features available",
"structure": "# Quickstart Guide\n## Layout Structure\nLayouts are defined in JSON format with the following structure:\n- Every layout is an array of JSONs\n- Every JSON represents a section, and can have the following fields:\n - `title` (string): Optionally display title for the section\n - `hidden` (boolean): Optionally hide entire section\n - `layout` (object): Optionally change the layout from vertical to horizontal\n - `direction` (string, required): Use 'horizontal' to change to horizontal layout\n - `wrap` (boolean): Optionally disable components wrapping and use a horizontal scrollbar\n - `components` (object[], required): \n**Example:**\n```json\n[\n {\n 'title': 'Section Title',\n 'hidden': true,\n 'layout': {\n 'direction': 'horizontal',\n 'wrap': false\n },\n 'components': [\n {\n 'type': 'text',\n 'key': 'nameInput1',\n 'title': 'Full Name',\n 'placeholder': 'Enter your name...',\n 'tooltip': 'Please also include your middle name',\n 'required': true,\n 'hidden': false\n }\n ]\n }\n]\n```",
"Components-into+text": "## Components Library\n### Common Properties\nAll components support these base properties:\n- `key` (string, required): Unique identifier for the field\n- `type` (string, required): Component type identifier\n- `title` (string): Display title for the field\n- `tooltip` (string): Hover tooltip text\n- `hidden` (boolean): Whether the component should be hidden\n- `required` (boolean): Whether the field is required\n- `hierarchy` (object): Conditional visibility rules\n - `condition` (string): DQL condition to evaluate\n---\n### Input Components\n#### Text Input\n- Type: `text`\n- Properties:\n - All common properties\n - `placeholder` (string): Placeholder text\n - `disabled` (boolean): Whether the field is disabled\n - `errorMessage` (string): Error message to display\n\n*Example:*",
"Components-select": "---\n#### Single Selection - Dropdown\n- Type: `select`\n- Properties:\n - All common properties\n - `options` (array, required): Array of options\n - `label` (string): Display text\n - `value` (any): Option value\n - `disabled` (boolean): Whether the field is disabled\n\n*Example:*",
"Components-raido": "---\n#### Single Selection - Radio Buttons \n- Type: `radio`\n- Properties:\n - All common properties\n - `options` (array, required): Array of options\n - `label` (string): Display text\n - `value` (any): Option value\n - `disabled` (boolean): Whether the field is disabled\n\n*Example:*",
"Components-checkboxes": "---\n#### Multiple Selection - Checkboxes\n- Type: `checkbox`\n- Properties:\n - All common properties\n - `options` (array, required): Array of options\n - `label` (string): Display text\n - `value` (any): Option value\n - `disabled` (boolean): Whether the field is disabled\n\n*Example:*",
"Components-slider": "---\n#### Number Single Selection - Slider\n- Type: `slider`\n- Properties:\n - All common properties\n - `min` (number): Minimum value\n - `max` (number): Maximum value\n - `default` (number): Default value\n - `step` (number): Step increment\n - `disabled` (boolean): Whether the field is disabled\n\n*Example:*",
"Components-rating": "---\n#### Number Single Selection - Star Rating\n- Type: `rating`\n- Properties:\n - All common properties\n - `maxStars` (number): Maximum number of stars (default: 5)\n - `showValue` (boolean): Whether to show numeric value\n\n*Example:*",
"Components-image": "---\n### Media Components\n#### Image Viewer\n- Type: `image`\n- Properties:\n - All common properties\n\n*Example:*",
"image": "https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/b/b9/MagrittePipe.jpg",
"Components-audio": "---\n#### Audio Viewer\n- Type: `audio`\n- Properties:\n - All common properties\n\n*Example:*",
"audio": "https://cms-public-artifacts.artlist.io/content/music/aac/958142_Clair_du_Lune_-Debussy-_-_Master_v1_-_No_Bpm_-_020125__-_BOV_-_ORG_-_RMS_-_2444.aac",
"Components-video": "---\n#### Video Viewer\n- Type: `video`\n- Properties:\n - All common properties\n\n*Example:*",
"video": "https://videos.pexels.com/video-files/856171/856171-hd_1920_1080_30fps.mp4",
"Components-url": "---\n#### URL Viewer\n- Type: `url`\n- Properties:\n - All common properties\n - `initialWidth` (number): Initial iframe width\n - `initialHeight` (number): Initial iframe height\n\n*Example:*",
"url": "https://www.google.com",
"Components-markdown": "---\n#### Markdown Viewer\n- Type: `markdown`\n- Properties:\n - All common properties\n- Insert the markdown text as the value of the markdown component key\n\n*This entire layout is an example*",
"Components-conversation": "---\n### Special Components\n#### Conversation\n- Type: `conversation`\n- Properties:\n - All common properties\n- Insert the conversation data as the value of the `convesation` component key, in the form of a JSON object[], and the following fields:\n - `role` (string): Use the word 'user' for the right bubble, or any other string for the left bubble title.\n - `content` (string): The bubble text.\n\n*Example:*",
"conversation": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "Hello!"
},
{
"role": "assistant",
"content": "Hi there! How can I help you today?"
}
],
"Components-condition": "---\n### Visibility Control\nComponents and sections can be hidden in three ways:\n1. **Direct hiding**: Use the `hidden` property\n```json\n{\n 'type': 'text',\n 'key': 'hiddenField',\n 'hidden': true\n}\n```\n2. **Hierarchical fields**: Make visibility conditional on other field values\n```json\n{\n 'type': 'radio',\n 'key': 'parentField',\n 'title': 'Click to show',\n 'options': [\n {\n 'label': 'Show',\n 'value': 'true'\n }\n ]\n},\n{\n 'type': 'image',\n 'key': 'childField',\n 'hierarchy': {\n 'condition': { 'parentField': { '$eq': 'true' } }\n }\n}\n```\n*Example:*",
"childField": "https://media1.tenor.com/m/uXZQf0CcrSQAAAAd/tada-ta.gif",
"Components-more-conditions": "*More examples:*\n- Show if riddle answer contains 'raven':\n```json\n{\n 'condition': { 'riddle_answer': { '$ilike': '*raven*' } }\n}\n```\n- Use AND logic to show if tea party size is 42 and time is frozen:\n```json\n 'condition': {\n '$and': [\n {\n 'tea_party_size': {\n '$eq': '42'\n }\n },\n {\n 'time_frozen': true\n }\n ]\n }\n```\n- Use OR logic to show if tea party size is 42 or time is frozen:\n```json\n{\n 'condition': {\n '$or': [\n {\n 'tea_party_size': {\n '$eq': '0'\n }\n },\n {\n 'tea_party_size': {\n '$eq': 'infinity'\n }\n }\n ]\n }\n}\n```\n- Use IN logic to show if tea party size is 0, 42 or infinity:\n```json\n{\n 'condition': {\n 'tea_types': {\n '$in': ['earl_grey', 'darjeeling']\n }\n }\n}\n```\n- Use EXISTS logic to show if tea party size is not 0:\n```json\n{\n 'condition': {\n 'riddle_answer': {\n '$exists': true\n }\n }\n}\n```\n- Advance exmaple:\n```json\n{\n 'condition': {\n '$or': [\n {\n '$and': [\n {\n 'tea_party_size': {\n '$eq': '6'\n }\n },\n {\n 'time_frozen': true\n }\n ]\n },\n {\n '$and': [\n {\n 'tea_types': {\n '$in': ['chamomile']\n }\n },\n {\n 'riddle_answer': {\n '$exists': true\n }\n }\n ]\n }\n ]\n }\n}\n```\n3. **Dynamic hiding**: Use JavaScript to control visibility\n```javascript\nmodule.exports = {\n run: async function (formData, formLayout) {\n // Hide field based on some condition\n formLayout[0].components[0].hidden = someCondition;\n return {\n formData,\n formLayout,\n };\n },\n};\n```\n",
"js-css": "---\n## JavaScript and CSS for Dynamic Behavior\n### JavaScript Module\nAdd custom validation and dynamic behavior by providing a JavaScript module:\n```javascript\nmodule.exports = {\n run: async function (formData, formLayout) {\n // Modify form data or layout\n return {\n formData: modifiedData,\n formLayout: modifiedLayout,\n };\n },\n};\n```\n### Custom CSS\nAdd custom styling by providing CSS:\n```css\n.form-section {\n /* Custom section styling */\n}\n\n.field-container {\n /* Custom field styling */\n}\n```\n---\n *Find more examples in our Template Library*."
}JavaScript
In the GenAI Multimodal Recipe of the Dataloop platform, the JavaScript section plays a powerful and flexible role—especially in the context of the Evaluation Studio. This capability allows teams to extend form behaviors and interactivity with custom logic directly embedded in the recipe layout.
The JavaScript section enables dynamic customization of the annotation interface by providing a run() function that the Dataloop system executes each time:
Form data is changed by the annotator
The form is initialized or updated
Custom logic needs to react to user input
This allows you to enforce validation, transform layout, and communicate with the platform, all in real-time.
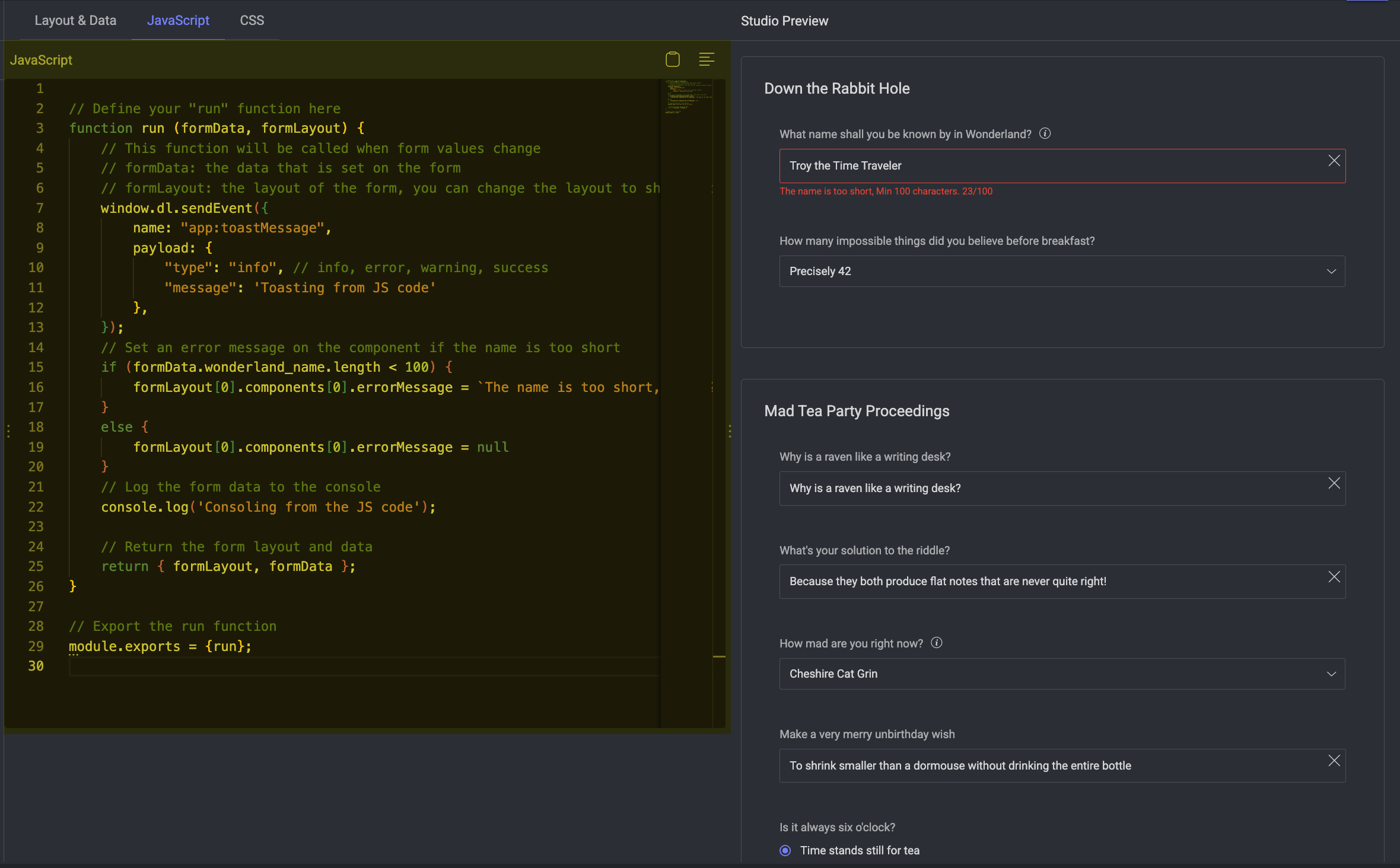
For example,
// Define your "run" function here
function run (formData, formLayout) {
// This function will be called when form values change
// formData: the data that is set on the form
// formLayout: the layout of the form, you can change the layout to show error messages or other ui elements
window.dl.sendEvent({
name: "app:toastMessage",
payload: {
"type": "info", // info, error, warning, success
"message": 'Toasting from JS code'
},
});
// Set an error message on the component if the name is too short
if (formData.wonderland_name.length < 100) {
formLayout[0].components[0].errorMessage = `The name is too short, Min 100 characters. ${formData.wonderland_name.length}/100`
}
else {
formLayout[0].components[0].errorMessage = null
}
// Log the form data to the console
console.log('Consoling from the JS code');
// Return the form layout and data
return { formLayout, formData };
}
// Export the run function
module.exports = {run};
Use cases
1. Custom Validation
You can check user input and set error messages dynamically:
// 🔍 Check if the 'username' field in the form has less than 10 characters
if (formData.username.length < 10) {
// ⚠️ If the condition is true, set a validation error message on the first component
// in the first form layout block
formLayout[0].components[0].errorMessage = 'Username too short';
}2. Dynamic UI Feedback
You can display real-time feedback using platform-integrated mechanisms like toast notifications:
// 🔔 Trigger a toast notification in the Dataloop UI
window.dl.sendEvent({
// Name of the built-in event that shows a toast
name: 'app:toastMessage',
// Data payload passed to the event handler
payload: {
type: 'info', // Toast category: 'info' | 'success' | 'warning' | 'error'
message: 'Input received!' // Text that will appear in the toast banner
}
});3. Conditional UI Modification
You can show/hide fields, change values, or even inject new UI components based on logic:
// Check if the 'enableAdvanced' field in the form data is set to true
if (formData.enableAdvanced === true) {
// If true, make the second component (index 1) inside the third form section (index 2) visible
formLayout[2].components[1].visible = true;
}Platform Integration Capabilities
This JavaScript block isn’t sandboxed in isolation—it has access to the broader Dataloop context through:
window.dl.sendEvent(...)to emit internal UI events (like messages)formLayoutupdates to visually reflect logicReusable patterns to enforce consistency across annotation projects
CSS
In the Multimodal Layout Builder of the Dataloop platform, the CSS section is a styling layer that empowers you to fully customize the appearance of the annotation interface—specifically within the GenAI Evaluation Studio. This feature is designed to give you fine-grained control over the UI, helping to create a tailored and branded experience for evaluators, streamline usability, and improve cognitive focus for annotators working on complex GenAI outputs.
The CSS section allows you to inject custom styles into your recipe layout. This means you can override default component styles or add entirely new visual styles for specific annotation tasks.
By leveraging CSS, you can:
Highlight critical fields
Hide or dim less important UI elements
Enforce brand consistency
Improve readability for specific data types
Visually separate input/output sections
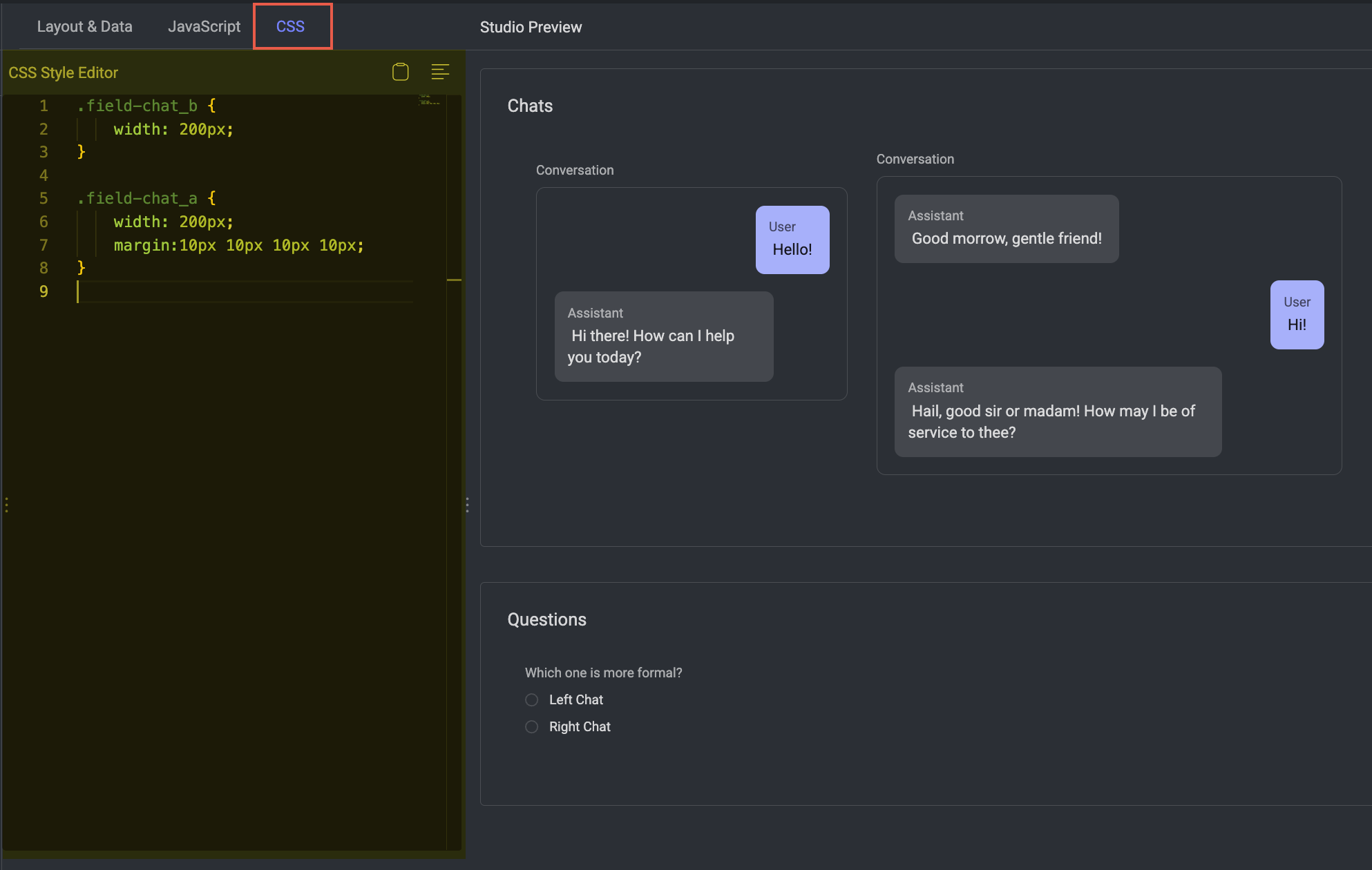
For example,
/* Set a fixed width of 200px for the form field with class 'field-chat_b' */
.field-chat_b {
width: 200px;
}
/* Set a fixed width of 200px for the form field with class 'field-chat_a' */
.field-chat_a {
width: 200px;
}
/* Style the title field:
- Font size set to 16px
- Font weight medium (500)
- Light gray color for text
- !important ensures these styles override any default styles
*/
.field-title {
font-size: 16px !important;
font-weight: 500 !important;
color: #f5f2f2 !important;
}
/* Apply a full width (100%) to all elements whose class starts with 'field-' */
[class^="field-"] {
width: 100%;
}Studio Preview
In the GenAI Multimodal Recipe Builder of the Dataloop platform, the Studio Preview section is an essential visual interface for developing and validating your GenAI Evaluation Studio workflows. It allows users to interactively inspect and test how the annotation UI will look and behave before publishing it to production.
The Studio Preview is designed to:
Visualize your current layout configuration
Simulate the actual user experience during annotation
Test the integration of Sample Data and JavaScript logic
Catch design or usability issues early.
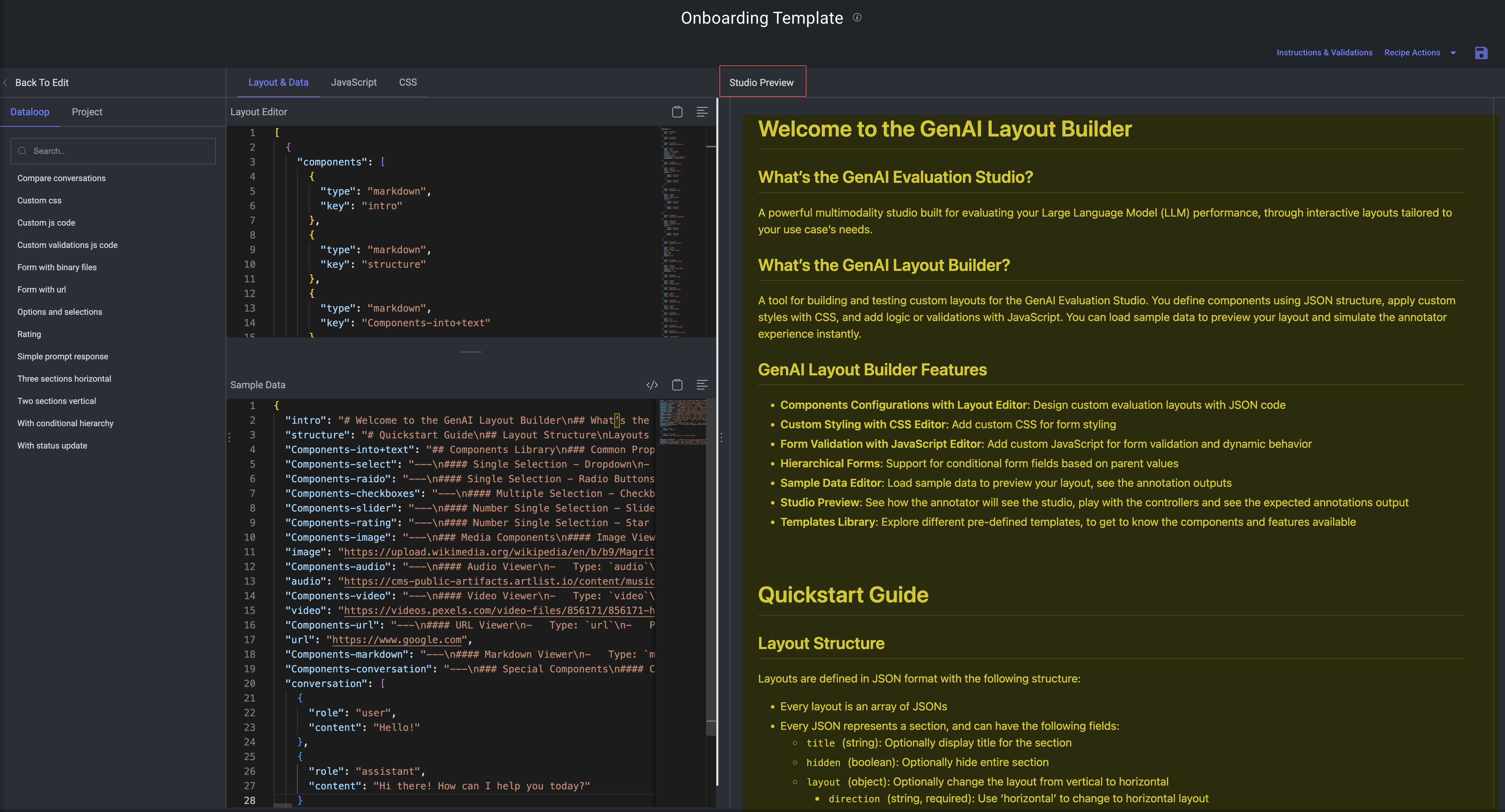
Components Library
The Components Library in the GenAI Multimodal Recipe of the Dataloop platform provides a set of configurable UI building blocks that are used to construct custom annotation interfaces in the GenAI Multimodal Studio. These components define the structure, functionality, and user experience of your annotation forms, enabling teams to design interfaces that match the logic and modality of any GenAI evaluation task—text, image, audio, video, chat, or multimodal combinations.
Each of these components is placed within layout sections, which are then displayed in the Studio Preview. You can combine multiple components to build:
A/B evaluations of generated content
Chat comparisons
Content classification or rating tasks
Image or audio-based grounding evaluations
Multi-field scoring forms
They work seamlessly with:
JavaScript logic (for dynamic behavior)
CSS styling (for UI customization)
Sample Data (for simulated previews)
All components support these base properties:
Property | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
| ✅ | Unique identifier for the component, used to reference it in |
|
| ✅ | Defines the component type (e.g., |
|
| ❌ | Label or title shown to the user above the field |
|
| ❌ | Help text shown on hover (useful for annotator guidance) |
|
| ❌ | Whether the field should be hidden from the view |
|
| ❌ | Marks the field as required before submission |
|
| ❌ | Logic rules that control conditional visibility of this component |
|
| ❌ | A DQL (Dataloop Query Language) expression to trigger visibility or logic |
Title
Property | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
All common properties | - | - | - |
|
| ❌ | Placeholder or help text |
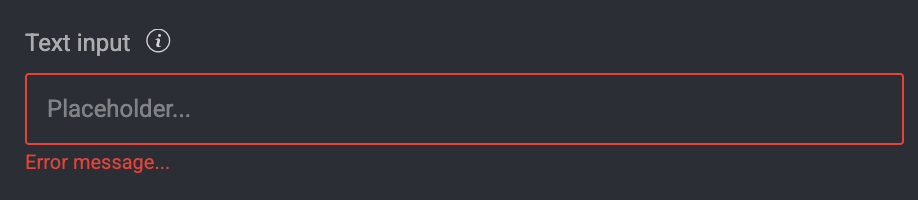
Text Input
Property | Type - | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
All common properties | - | - | - |
|
| ❌ | Placeholder text |
|
| ❌ | If true, the field is not editable |
|
| ❌ | Message shown on validation error |
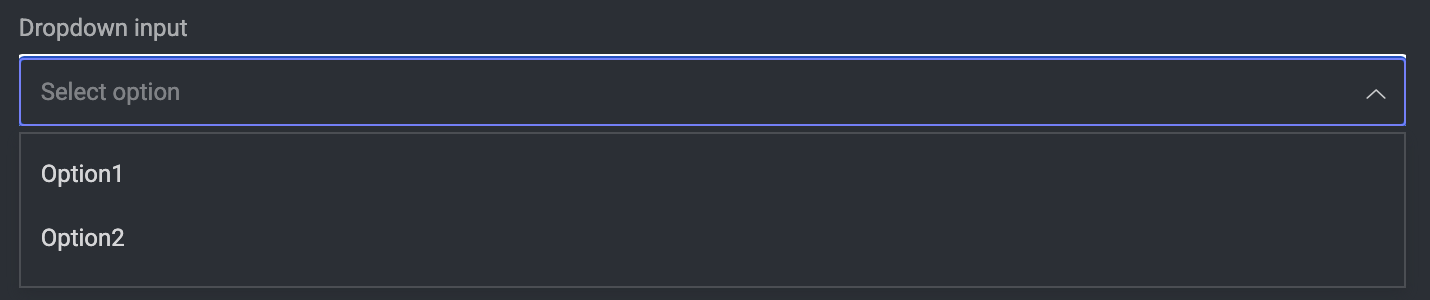
Single Selection - Dropdown
Property | Type - | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
All common properties | - | - | - |
|
| ✅ | List of choices |
|
| ❌ | Display text for each option |
|
| ❌ | The internal value for each option |
|
| ❌ | Whether the field is disabled |
Single Selection - Radio Buttons
Property | Type: | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
All common properties | - | - | - |
|
| ✅ | Array of radio button choices |
|
| ❌ | Display text for each choice |
|
| ❌ | Internal value for selected option |
|
| ❌ | Whether the field is disabled |
Multiple Selection - Checkboxes
Property | Type - | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
All common properties | - | - | - |
|
| ✅ | Array of checkbox choices |
|
| ❌ | Display text for each choice |
|
| ❌ | Value(s) selected |
|
| ❌ | Whether the field is disabled |
Number Single Selection - Slider
Property | Type - | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
All common properties | - | - | - |
|
| ❌ | Minimum value |
|
| ❌ | Maximum value |
|
| ❌ | Initial/default slider position |
|
| ❌ | Increment between values |
|
| ❌ | Whether the slider is disabled |
Number Single Selection - Star Rating
Property | Type - | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
All common properties | - | - | - |
|
| ❌ | Maximum number of stars (default: 5) |
|
| ❌ | Show numeric value next to stars |

Image Viewer
Type:
imageProperties:
All common properties

Audio Viewer
Type:
audioProperties:
All common properties
Video Viewer
Type:
videoProperties:
All common properties
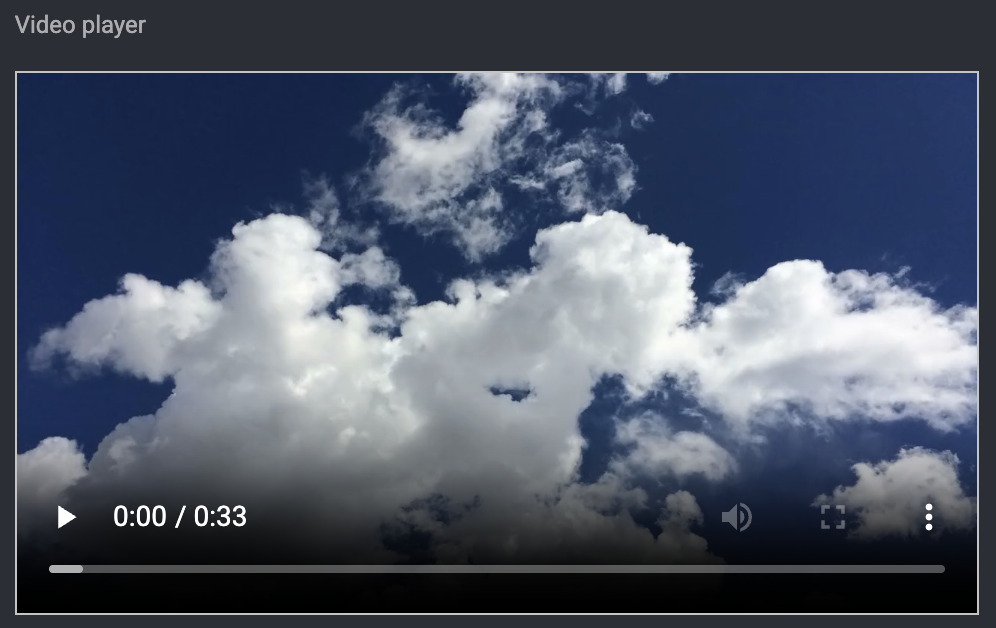
URL Viewer
Property | Type - | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
All common properties | - | - | - |
|
| ❌ | Width of the embedded iframe |
|
| ❌ | Height of the embedded iframe |
Markdown Viewer
Type:
markdownProperties:
All common properties
Insert the markdown text as the value of the markdown component key.
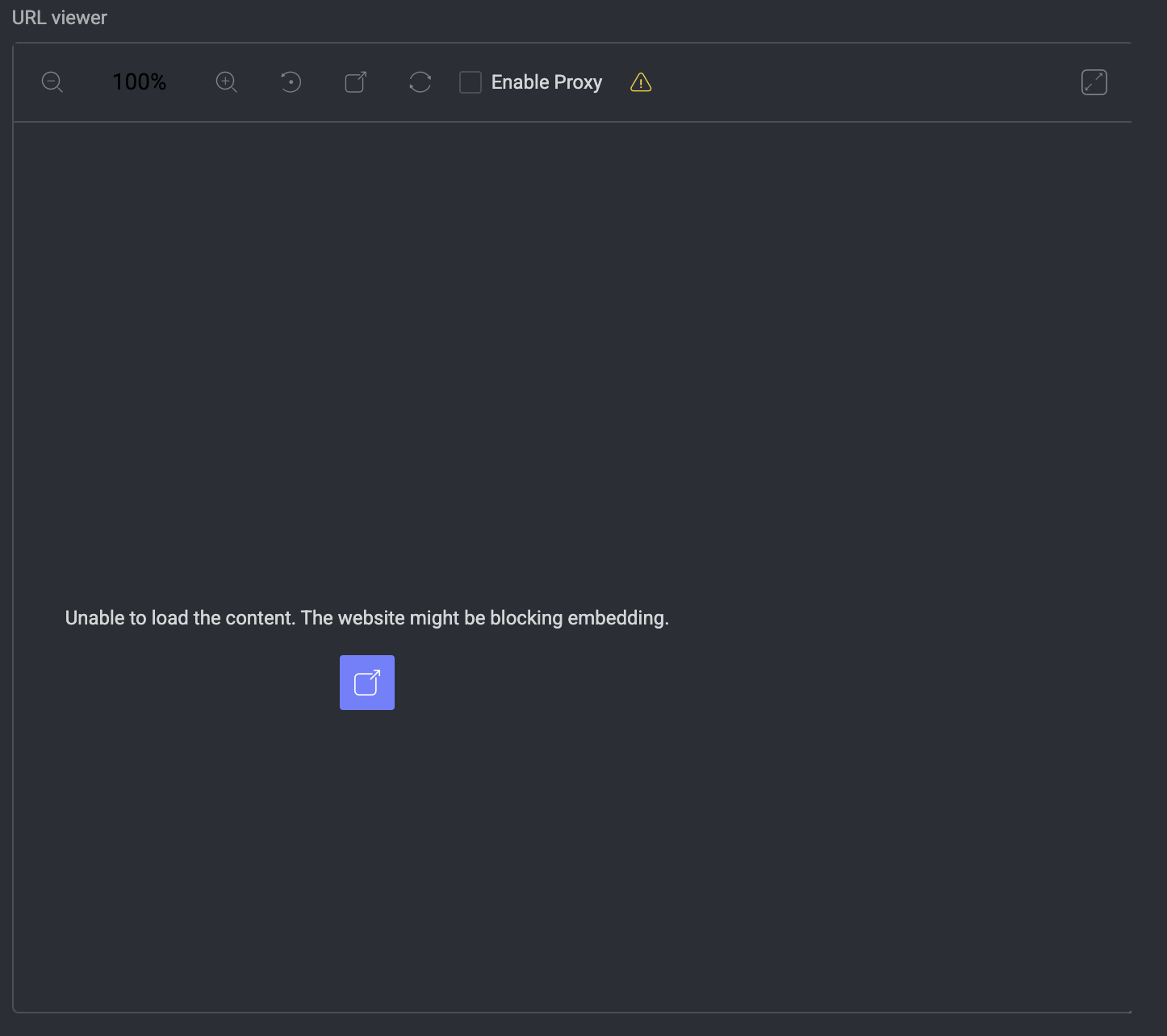
Conversation
Insert the conversation data as the value of the convesation component key, in the form of a JSON object[], and the following fields:
Property | Type - | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
All common properties | - | - | - |
|
| ❌ | Use the word ‘user’ for the right bubble, or any other string for the left bubble title. |
|
| ❌ | The bubble text. |
Recipe Creation Flow
Step 1. Design Your Multimodal Layout
Use the Multimodal Layout Builder to visually assemble your evaluation layout. Add components like:
Text input fields
Dropdowns, radio buttons, and checkboxes
Star rating widgets
Media viewers (image, audio, video)
LLM conversation displays
Custom markdown instructions or tips
Step 2. Define Form Logic and Behavior
Customize how the form responds to user interaction:
Show or hide fields dynamically based on inputs
Use conditional rules to guide form flow
Embed JavaScript for advanced logic and real-time feedback
Ensure data quality with:
Required fields for essential inputs
JavaScript-based validation for complex rules
Automatic blocking of invalid or incomplete submissions
Step 3. Style Your Interface
Apply custom CSS to fully control the look and feel of your form, ensuring it matches your brand and enhances usability.
Step 4. Create Sample Data & Verify in Studio Preview
Use the Sample Data section to populate the defined placeholders with sample data, then verify the results in the Studio Preview section.
Step 5. Assign the Recipe to the Datasets
Once the layout is complete, assign the Recipe to the required dataset.
Step 6. Start Using the GenAI Evaluation Studio
Upload a JSON (for example, an empty) file. Otherwise, add contents as per the format to get the data pre-populated.
Use the Multimodal Layout to run evaluations directly on your GenAI model outputs
Capture structured feedback, flags, and reviewer comments
Create GenAI / Multimodal Recipes
The Create Multimodal Recipe flow walks you from an empty project to a fully deployed evaluation form inside Dataloop’s GenAI Evaluation Studio.
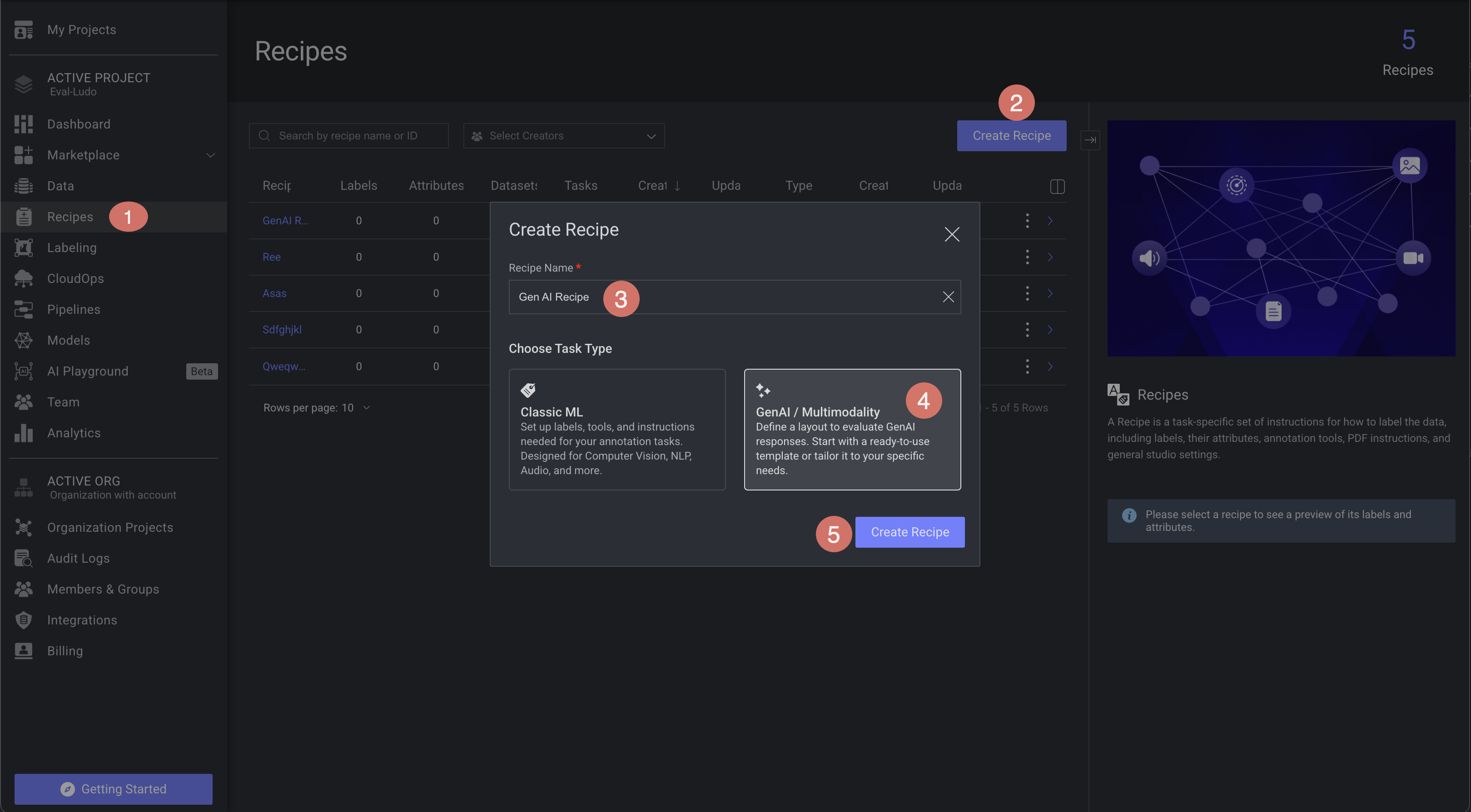
1. Launch the Recipe
Open Recipes from the left-hand navigation pane.
Click Create Recipe to bring up the configuration dialog.
Recipe Name – enter a unique, descriptive title.
Task Type – choose Gen AI / Multimodal.
Click Create Recipe. A confirmation toast appears, and you are taken to the Layout & Data editor.
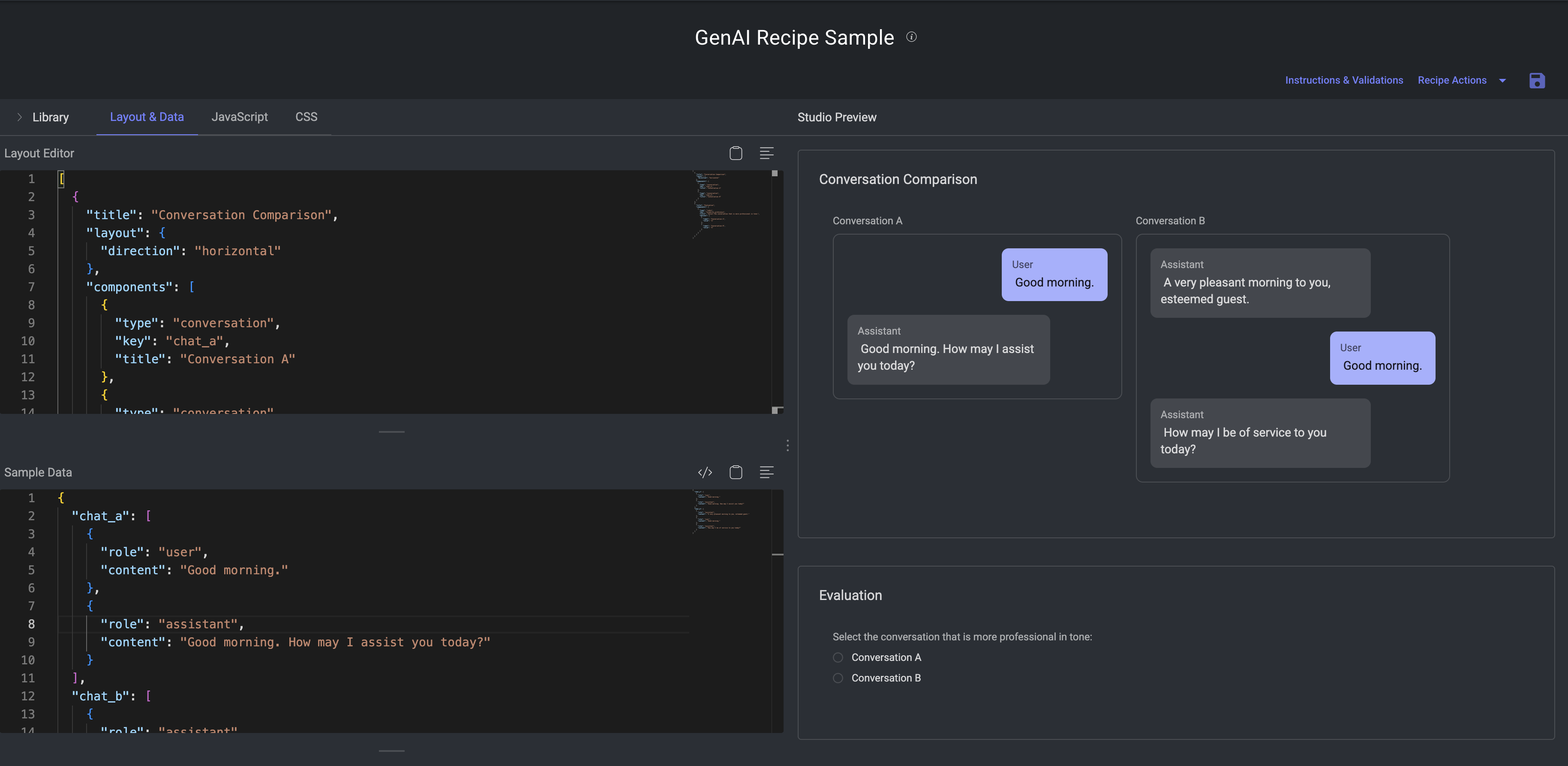
2. Design the Layout
The editor displays a sample format by default. Use your own scripts (including JavaScript and CSS), if required. Refer to the Components library to view various components and its properties can used to customize your recipe structure.
Otherwise, click on the Library tab to view and use the predefined Templates.
To use a template, follow steps below:
Select a template from the Library, and click Use Layout.
🚨 Once you confirm, the current form and layout will get overwritten by the selected template layout🚨 . Users can also check examples from the templates and copy and paste them to they own template (after clicking "back to edit").Click Use Layout to confirm it.
3. Generate Sample Data & Upload the JSON
After finalizing the layout, open the Sample Data section and click the
</>icon.A Python Usage Sample dialog appears containing an auto-generated script.
Click Copy to copy the code.
Run the script in your environment to upload a JSON data file into the target dataset while tagging it for evaluation-studio processing.
![]()
Click on the Copy icon to copy the python script and run the script to upload the
jsonfile to your dataset. Sample Python script is shown below:
import dtlpy as dl
import json
import io
# Get the dataset
dataset = dl.datasets.get(dataset_id='undefined')
# Create a io.BytesIO object from the data json
data = {
"chat_a": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "Hello!"
},
{
"role": "assistant",
"content": "Hi there! How can I help you today?"
}
],
"chat_b": [
{
"role": "assistant",
"content": "Good morrow, gentle friend!"
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": "Hi!"
},
{
"role": "assistant",
"content": "Hail, good sir or madam! How may I be of service to thee?"
}
]
}
buffer = io.BytesIO(json.dumps(data).encode('utf-8'))
buffer.name = '68404c727b5a5a853549a9a8-data.json'
buffer.seek(0)
item = dataset.items.upload(
local_path=buffer,
item_metadata={
'system': {
'shebang': {
'dltype': 'evaluation-studio'
},
'evaluation': {
'layoutName': '68404c727b5a5a853549a9a8'
}
}
}
)
print("Item uploaded successfully:", item.id)
print("Open in platform:", item.platform_url)
4. Save and Create the Recipe
Click Save
5. Run an Evaluation
Locate the uploaded JSON item in the dataset.
Open it with Multimodal Layout Studio.
The Studio loads your Multimodal Recipe, allowing reviewers to fill in responses, raise flags, and leave comments.
All inputs are validated automatically—basic required-field checks plus any JavaScript rules you added—blocking invalid submissions.
Templates Library
Let’s go a bit deeper into the most common built-in templates with examples available in the Library. There are two categories of recipes available:
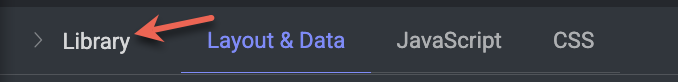
Dataloop: The list of available recipe templates by default.
Project: The list of recipes created and available in your project.
Start using one of the template by selecting it and clicking on the Use Layout. To customize the template, refer to the Componets Library and use them as required.
Compare Conversations
A layout designed to compare and analyze multiple conversations or text entries side by side. Compare two or more LLM responses side-by-side for quality, coherence, or factual accuracy.
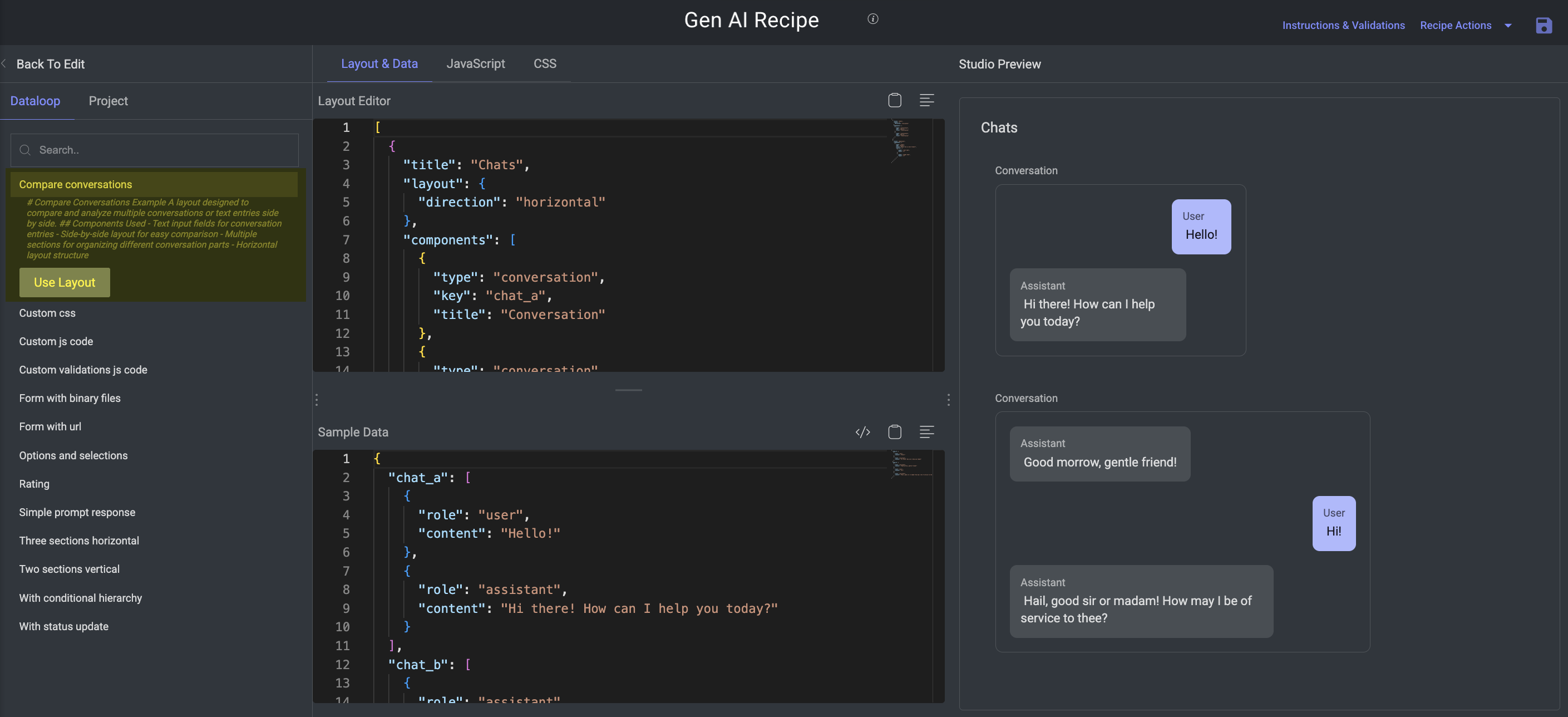
Components:
Text input fields for conversation entries
Side-by-side layout for easy comparison
Multiple sections for organizing different conversation parts
Horizontal layout structure.
Custom CSS
Purpose: Showcase how to fully customize the visual design of your evaluation forms using CSS.
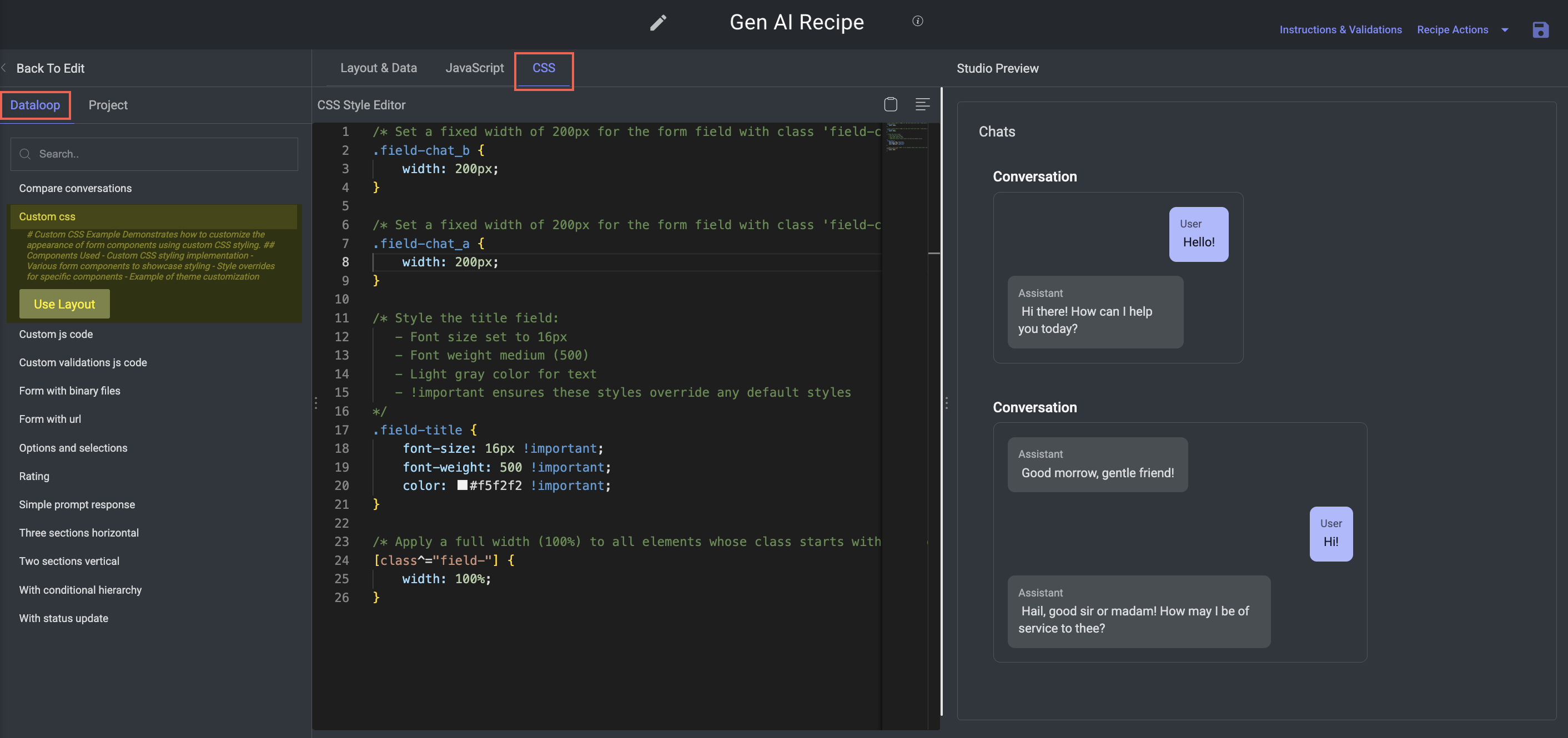
Key Features:
Tailors the form’s appearance using embedded CSS styles.
Helps apply consistent theming and branding across components.
Components:
Standard input components:
text,select, andcheckbox.Custom CSS styling for:
Theme colors (e.g., background, buttons, font)
Font styles (e.g., size, weight, family)
Component resizing (e.g., field widths, paddings)
Layout tweaks (e.g., spacing, alignment, positioning)
Custom JavaScript Code
Purpose: Demonstrate how to add advanced interactivity and validation logic to forms using custom JavaScript.
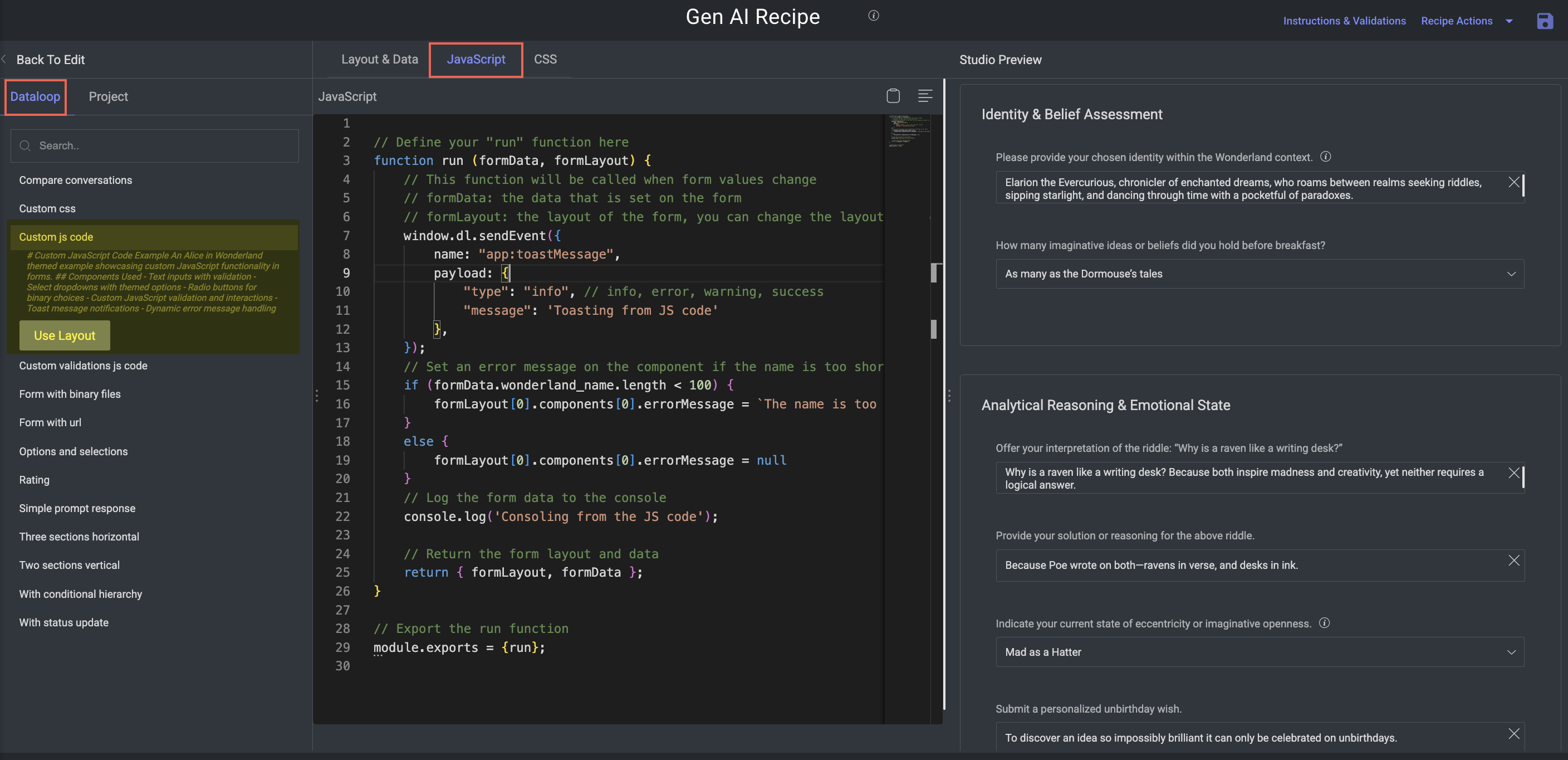
Key Features:
Enables real-time form behavior, conditionally interactive elements, and UI alerts.
Components:
Text inputs with live validation.
Select dropdowns with themed/predefined options.
Radio buttons for binary decisions.
Custom JS logic for:
Real-time validation
Dynamic error messages
Toast notifications (info/success/warning)
Interactive logic, e.g., show/hide based on other inputs
Example Behavior: Show/hide fields based on previous answers (e.g., enable advanced options only if a checkbox is selected).
Custom Validation JavaScript Code
Purpose: Focused example of using JavaScript purely for validation logic.
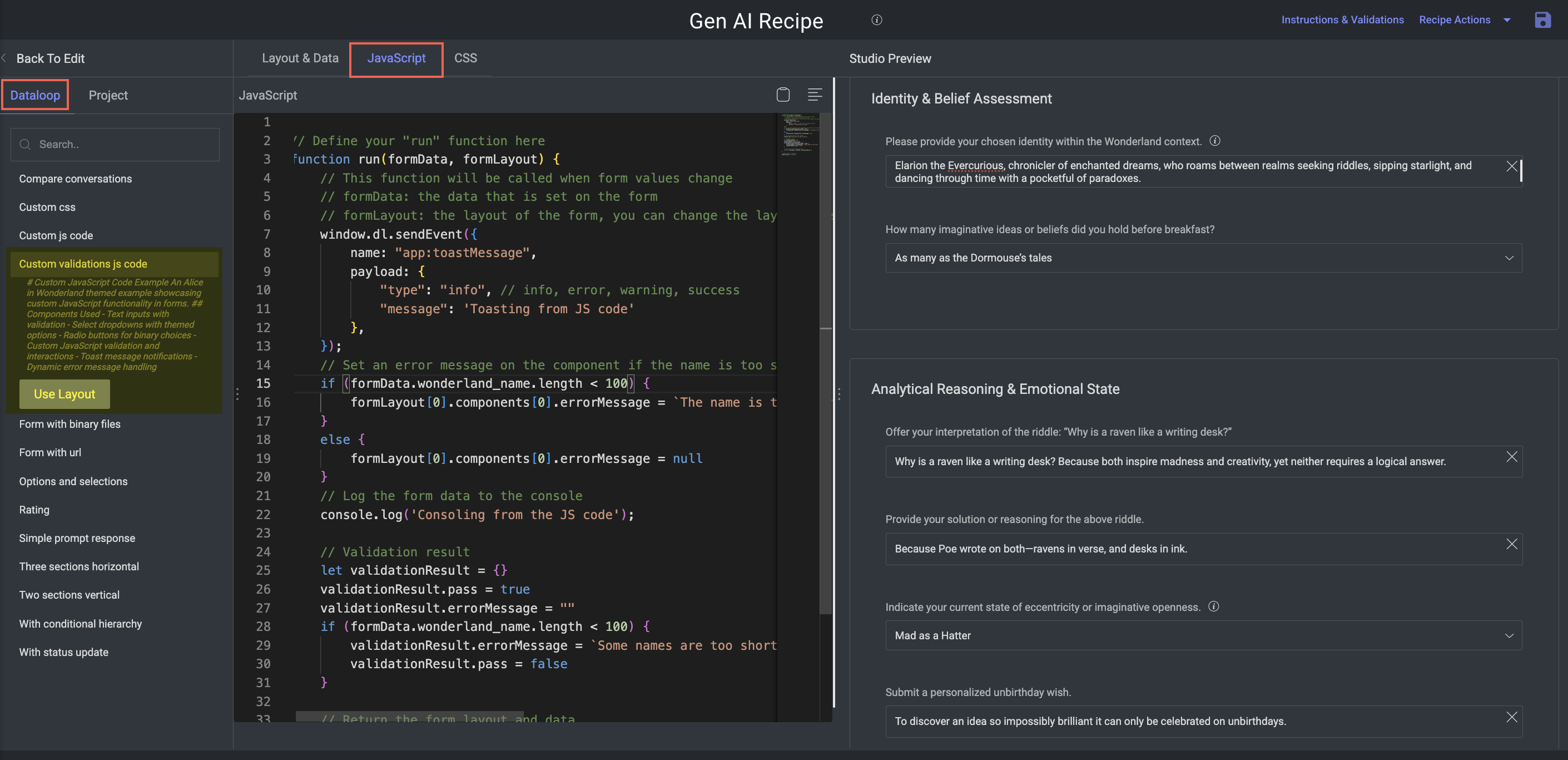
Key Features:
Demonstrates complex rule enforcement to ensure high-quality input before submission.
Components:
Multiple text fields and dropdowns with interdependent validation.
Pass/fail logic written in JavaScript.
Dynamic error messages based on input state.
Submission is blocked until all validations are satisfied.
Form with Binary Files
Purpose: Illustrates how to support uploading and validating binary content (media files) in forms.
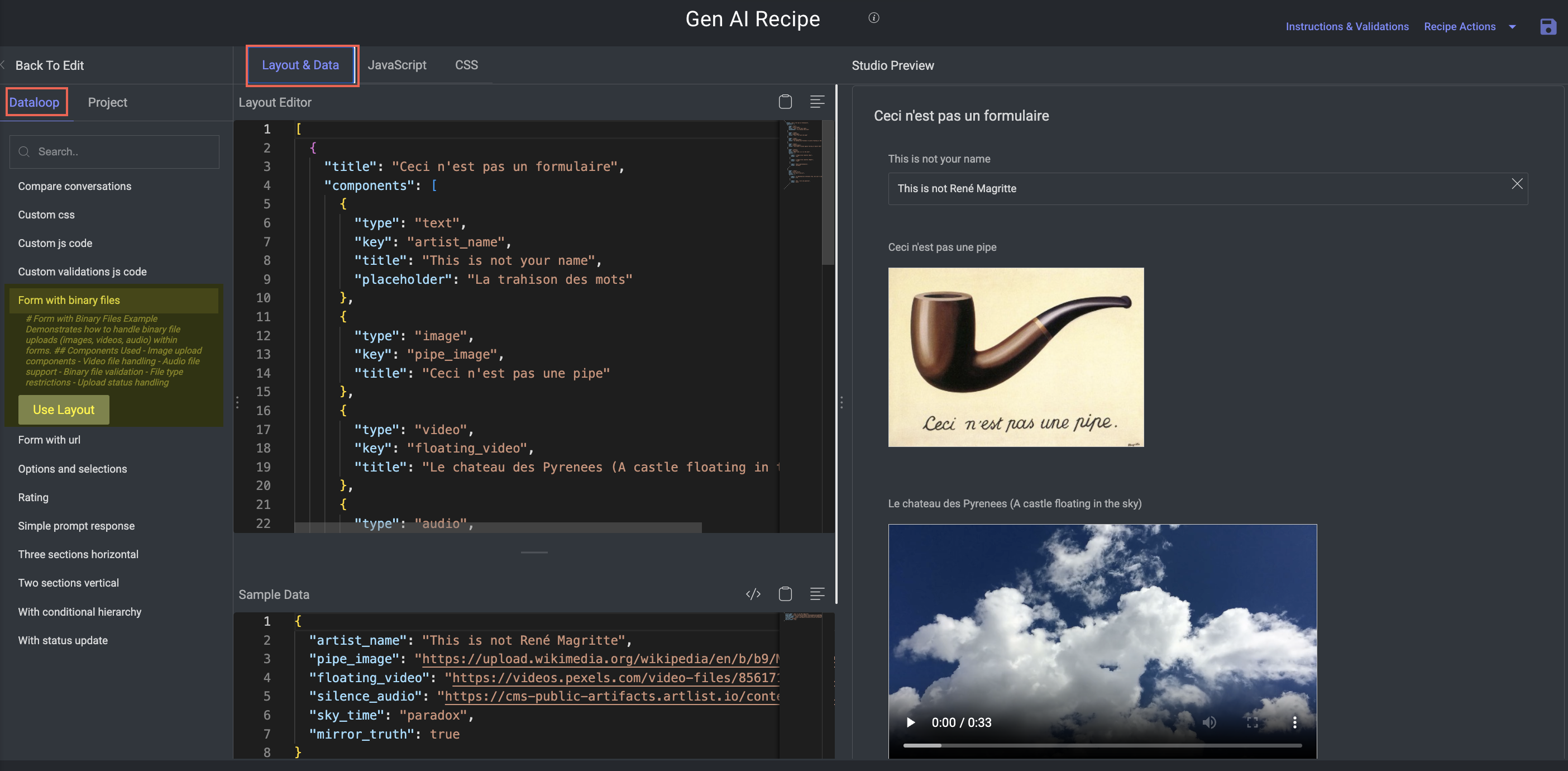
Key Features:
Ideal for image generation, multimodal output, or voice model evaluation tasks.
Components:
Image uploader
Audio/video file uploader
Built-in validations:
File format restrictions
Max file size
Upload tracking with progress indicators and status feedback
Form with URL
Purpose: Demonstrates how to evaluate or extract information from user-provided URLs.
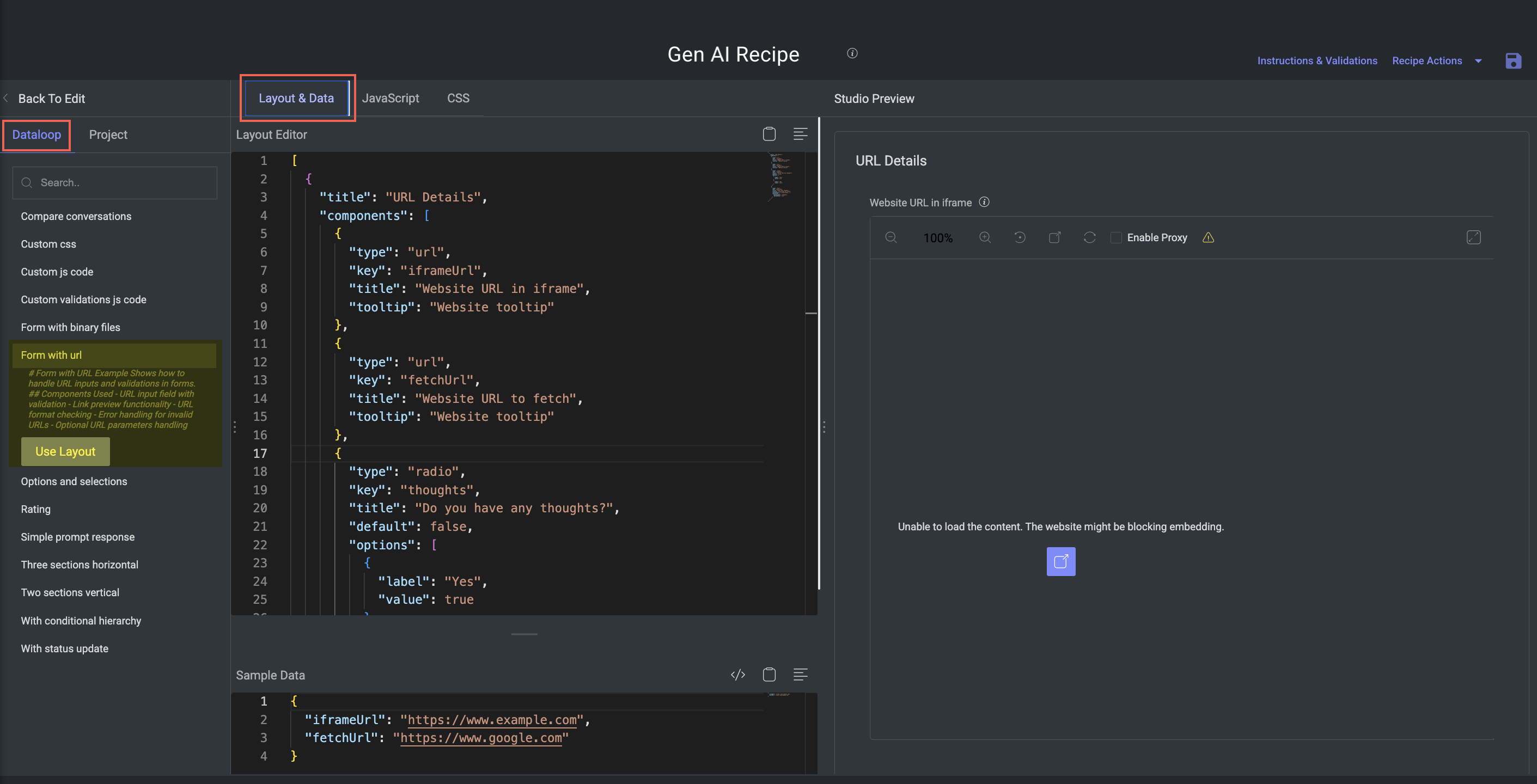
Key Features:
Useful for tasks involving external content, links to hosted outputs, or web-based tools.
Components:
URL input field with validation
Live link previews
Invalid URL detection with error messaging
Optional: parse query parameters from the URL for evaluation metadata
Options and Selections
Purpose: Present standard multiple choice selection mechanisms.
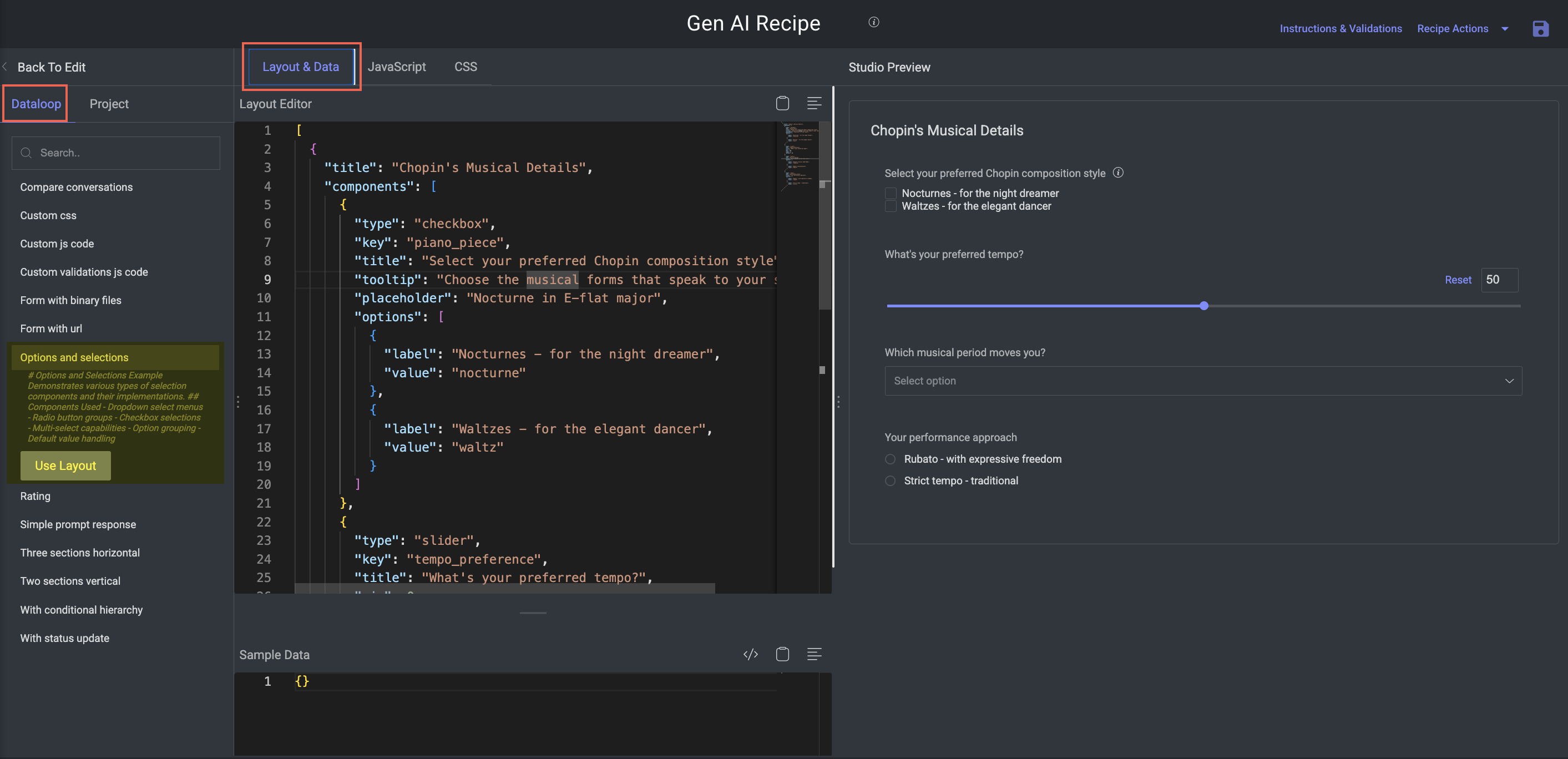
Key Features:
Commonly used in classification, preference ranking, or attribute tagging.
Components:
Dropdown menus (single select)
Radio button groups (mutually exclusive)
Checkbox groups (multi-select)
Default option settings
Grouped/structured option sets for better UX
Rating
Purpose: Collect quantitative and qualitative feedback using rating components.
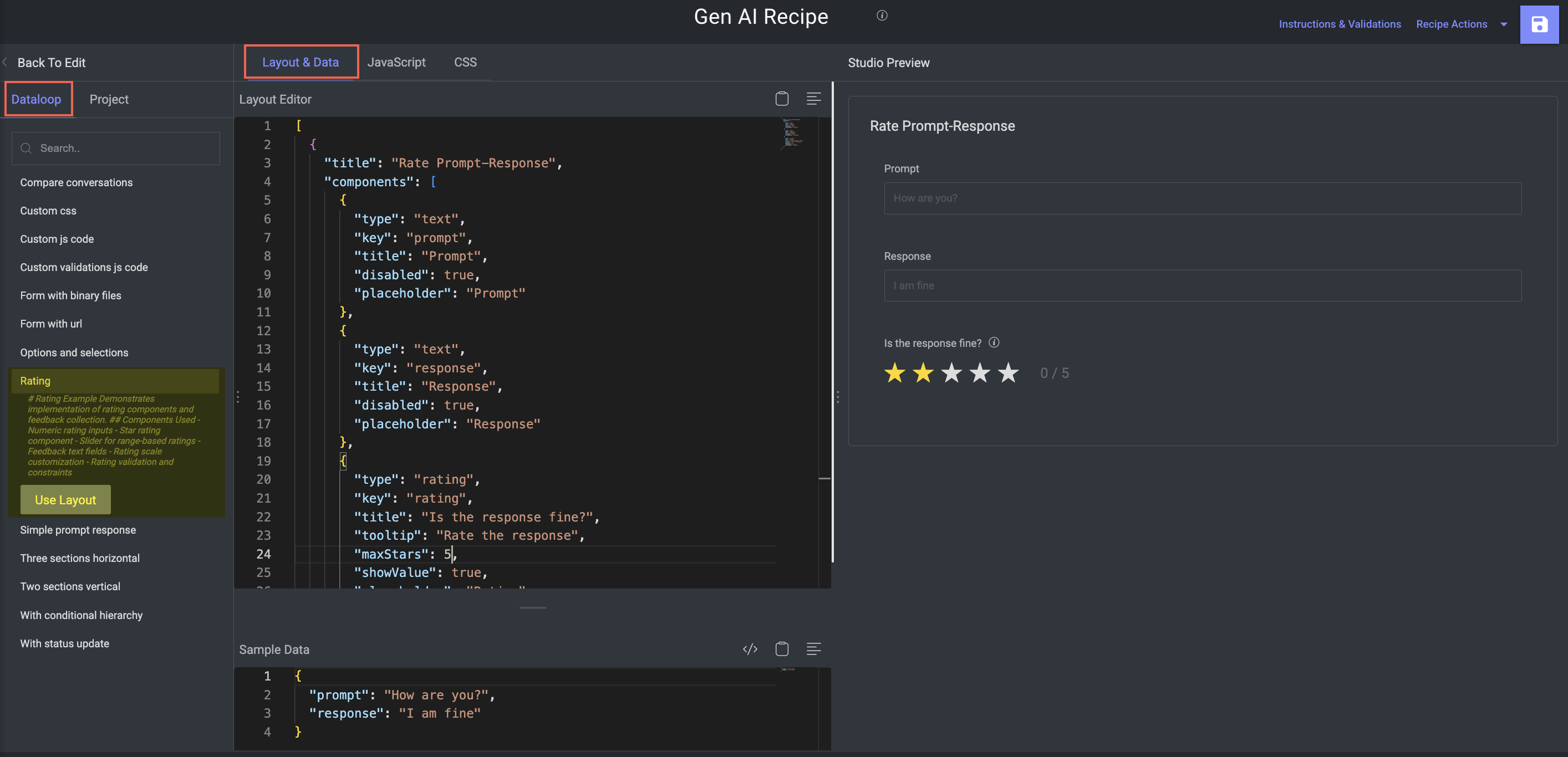
Key Features:
Used in model evaluation tasks like fluency, relevance, and safety scoring.
Components:
Star rating systems (1–5 or custom)
Numeric input fields for scores
Slider components for continuous ratings
Linked feedback text boxes
Min/max validation for scoring consistency
Simple Prompt Response
Purpose: Minimal example for evaluating prompt/response pairs.
.png)
Key Features:
Ideal for quick testing, dataset reviews, or basic output assessment.
Components:
Text input for the prompt
Text input for the model’s response
Clean layout with minimal validation
Three Sections Horizontal
Purpose: Compare three parallel outputs or inputs side-by-side in a single view.
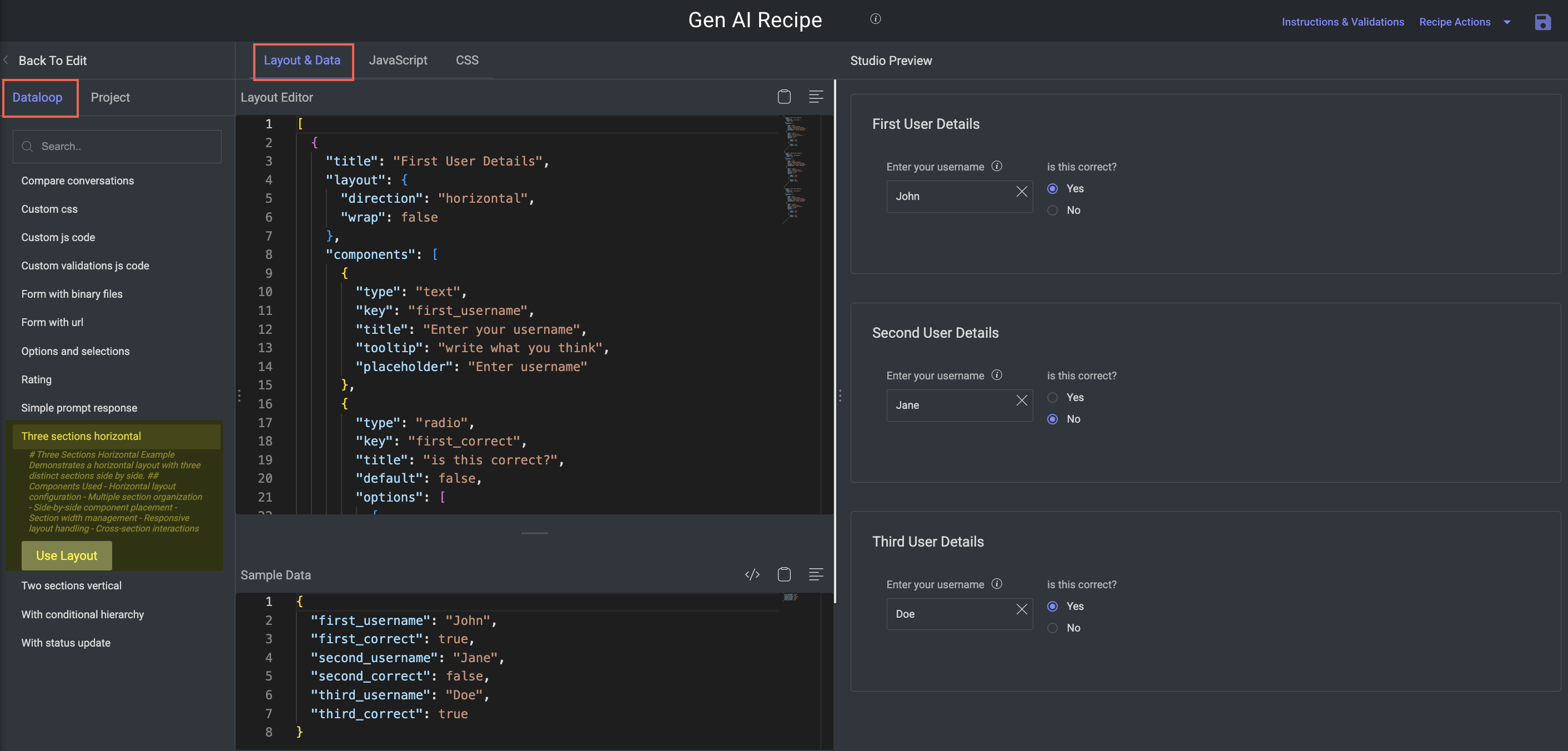
Key Features:
Great for comparing chatbot responses, image generations, or translated outputs.
Components:
Three horizontally laid-out sections
Equal column widths with responsive resizing
Optional interdependencies between sections
Two Sections Vertical
Purpose: Stack two sections vertically for a cleaner, linear annotation workflow.
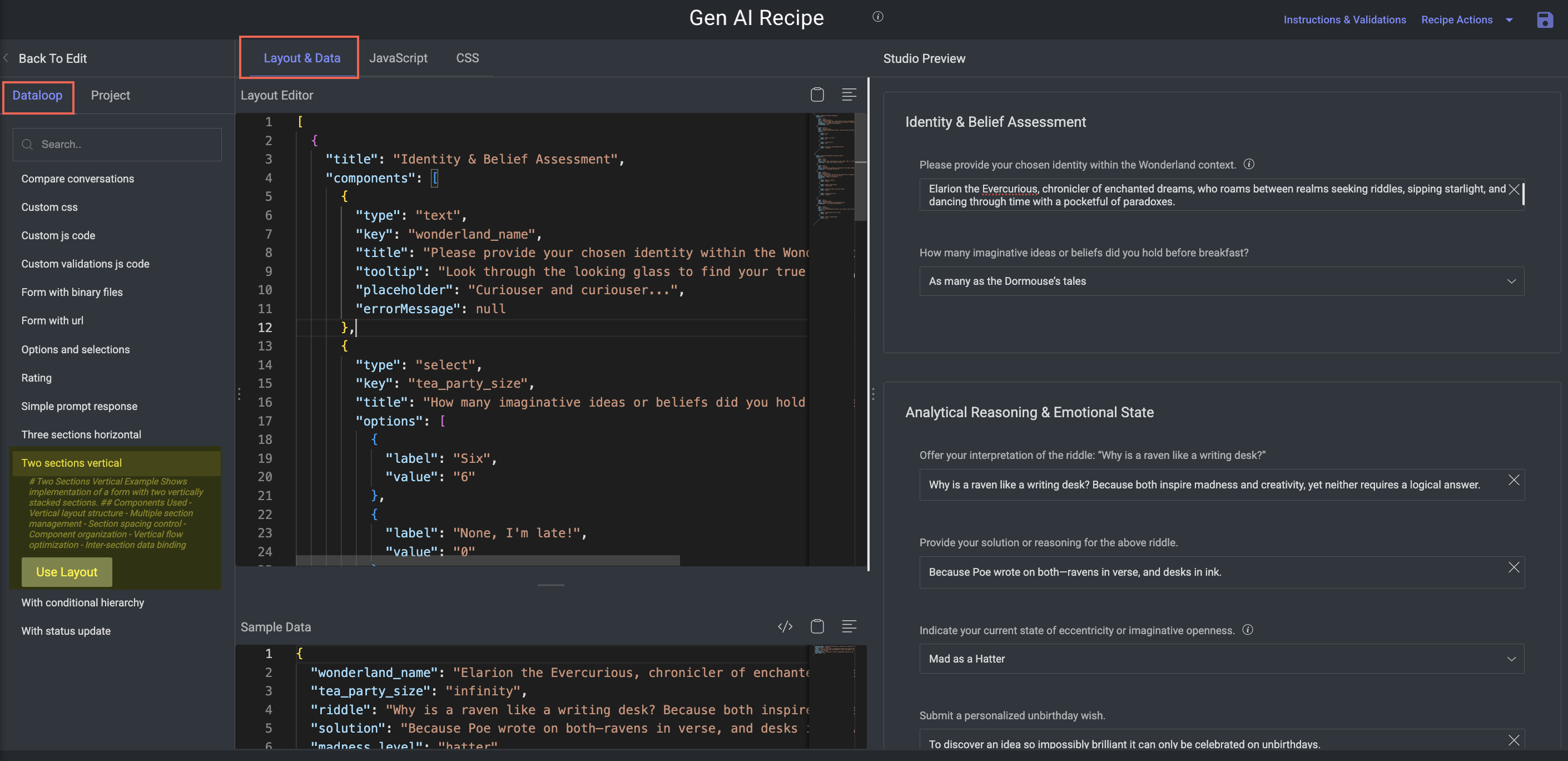
Key Features:
Simpler structure suited for prompt + output, before/after, or Q&A formats.
Components:
Vertically stacked layout
Logical separation between top/bottom sections
Controlled spacing for readability
With Conditional Hierarchy
Purpose: Show how to dynamically control form visibility based on input values.
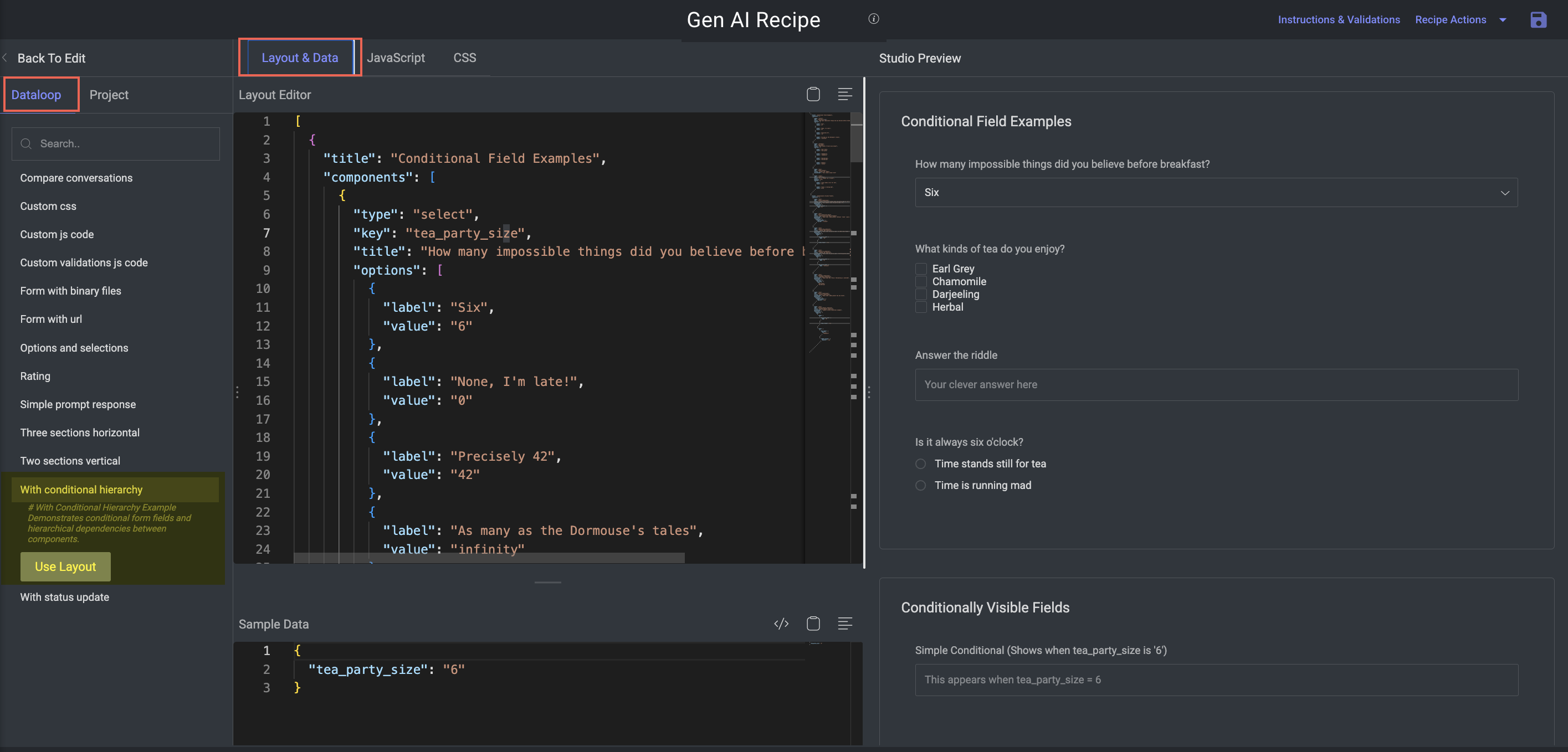
Key Features:
Powerful for adaptive forms, such as enabling advanced settings conditionally.
Components:
Hierarchical logic using
hierarchyorconditionfieldsSupports logical operators:
AND,OR,IN,EXISTS, etc.Multi-level visibility rules (e.g., show fields only if several conditions are met)
With Status Update
Purpose: Demonstrates state tracking and progress management within the form.
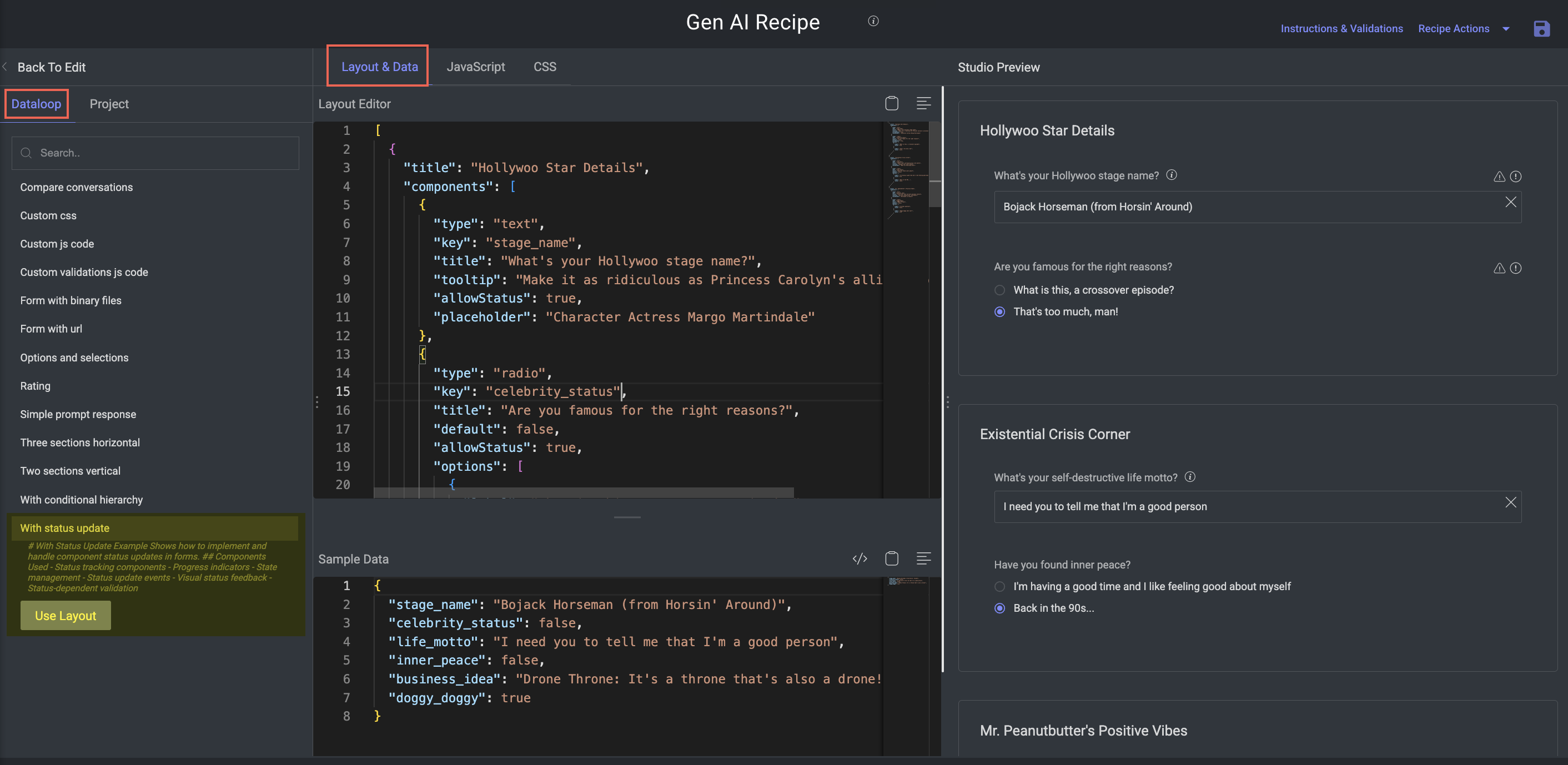
Key Features:
Enables interactive workflows where the status changes based on annotator inputs or stages.
Components:
Fields for status labels or dropdowns
Progress indicators or step-based feedback
Event-triggered status changes
Visual cues for "in progress", "complete", "needs review", etc.
Instructions and Validations
The Instructions and Validations section of a Multimodal Recipe empowers you to define and enforce clear guidelines and data quality checks directly within the Dataloop Annotation Studio. It helps standardize the annotation process, support quality assurance (QA), and block invalid submissions through custom validation logic.
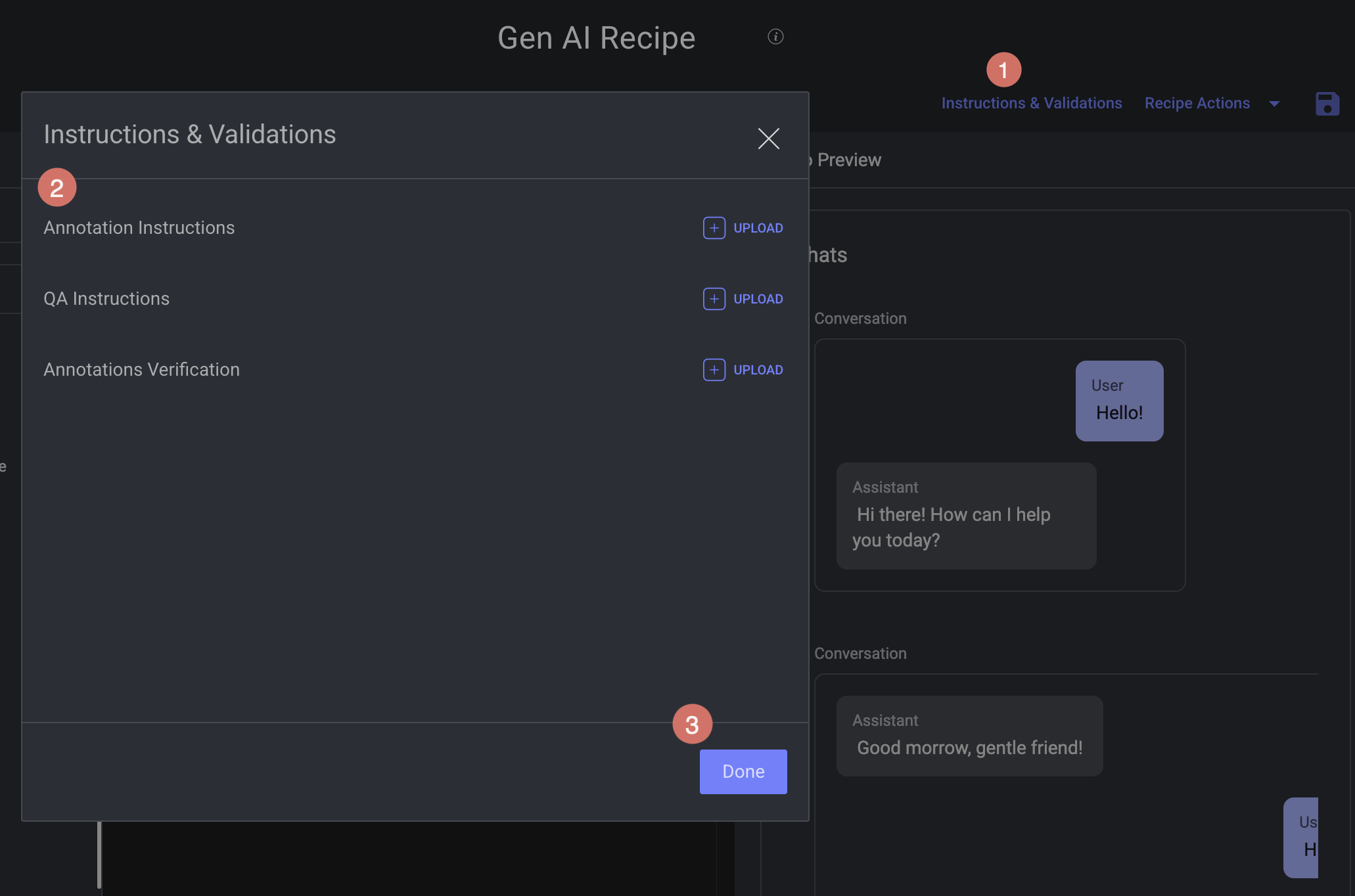
Upload Annotation Instructions
You can upload annotation guidelines directly into the Recipe. This allows annotators to easily access official instructions directly within the Annotation Studio while performing their tasks.
Supported Format: PDF
Display: Rendered inside the annotation interface for quick reference.
Purpose: Ensure annotation consistency and standardization across the team.
When you create a labeling task, you can select a specific range of pages from the PDF.
To upload:
Open your recipe, and click Instructions & Validations.
Click Upload next to the Annotation Instructions, and upload the PDF.
Click Done.
Upload QA Instructions
Quality Assurance guidelines can also be uploaded as a PDF document to the Recipe. QA reviewers will see these instructions within the Annotation Studio during quality control activities.
Supported Format: PDF
Display: Embedded into the QA interface for easy reviewer access.
Purpose: Help reviewers follow standardized quality check procedures.
When you create a QA task, you can select a specific range of pages from the PDF. If there is no QA Instructions PDF document, the annotation instruction PDF document is displayed.
Upload Annotation Verification (JS Scripts)
The Annotation Verification feature allows you to enforce complex data validation rules during annotation work by integrating custom JavaScript verification scripts directly into the Recipe settings.
When a JavaScript verification script is uploaded, it will automatically execute when the annotator clicks the COMPLETE button. This ensures that all required data quality standards are met before annotations can be submitted, preventing invalid or inconsistent data from entering production workflows.
Supported Format: JavaScript (
.js)Execution Trigger: When attempting to complete the annotation task.
Purpose:
Validate annotations before submission.
Enforce complex business rules or project-specific validations.
Prevent incomplete or incorrect submissions by blocking completion until conditions are met.
Common Use Cases for Verification Scripts
Annotation Verification Scripts can enforce a wide range of business and data quality rules, including but not limited to:
1️⃣ Label Coexistence Rules
Example: Limit the number of specific annotations.
Use Case: Prevent having more than a defined number of annotations with a particular label.
Sample Rule: A maximum of 3 annotations with the label
Personis allowed in a single item.
2️⃣ Cross-Label and Attribute Dependencies
Example: Enforce relationships between different labels and attributes.
Use Case: Prevent conflicting annotations from co-existing in the same dataset item.
Sample Rule: If there is an annotation with label
Vehicleand attributeType = Car, there cannot also be an annotation with labelBicycleand attributeType = Electricon the same image.
3️⃣ Tool-Specific Geometric Rules
Example: Enforce geometry validations based on annotation tool outputs.
Use Case: Ensure spatial relationships between different annotations.
Sample Rule: A
Keypointannotation must always reside within the boundaries of aBounding Boxannotation.
Learn more and see JS code examples.