Integrations securely connect to data providers like AWS, GCP, and Azure, ensuring flexible access while managing authentication, authorization, and secret storage. They prioritize security, reliability, and compliance for safe data management.
AWS: Why Cross-Account Integration is the Best Choice?
The Least privilege principle: AWS Cross-Account integration empowers you to grant finely-tuned IAM roles and permissions to users or service accounts across different AWS accounts. This enables you to restrict access to specific actions and resources, thereby minimizing the attack surface in the event of a compromise.
Rotational capability: With AWS Cross-Account, you have the flexibility to effortlessly rotate IAM roles. This facilitates periodic refreshment of the credentials used by a third-party service, a significantly more secure approach compared to the use of long-lived access keys that persist until you revoke them.
Better auditability: AWS Cross-Account integration produces comprehensive logs of all actions taken by the third-party service, facilitating more effective monitoring and detection of any suspicious activity. This gives you better visibility and control over third-party access to your AWS resources.
Separation of responsibilities: The Cross-Account feature in AWS allows you to maintain control over your AWS accounts and delegate specific tasks to third-party services without exposing your credentials. This ensures that third-party services only have access to the resources they require for their tasks, thus minimizing the risk of credential theft or misuse.
In conclusion, the use of AWS Cross-Account integration instead of Access Key or STS integrations offers a more secure and flexible mechanism for granting access to third-party services in AWS. It allows you to implement the principle of least privilege, easily rotate credentials, and provide better auditability and separation of responsibilities.
To learn how to do this, see the AWS Cross Account Integration article.
GCP: Why Cross-Project Integration is the Better Choice?
The Least privilege principle: Cross-Project access in GCP allows you to grant fine-grained IAM roles and permissions to users or service accounts across different GCP projects. This means you can restrict access to specific actions and resources, reducing the attack surface in case the third-party service is compromised.
Rotational capability: Cross-Project access in GCP enables you to easily rotate IAM roles, allowing you to periodically refresh the credentials used by a third-party service. This is a more secure approach than using long-lived access keys that persist until you revoke them.
Better Audibility: Cross-Project access in GCP generates detailed logs of all actions taken by the third-party service, making it easier to monitor and detect suspicious activity. This provides better visibility and control over third-party access to your GCP resources.
Separation of responsibilities: The Cross-Project access in GCP enables you to maintain control over your GCP projects and delegate specific tasks to third-party services without exposing your credentials. This ensures that third-party services only have access to the resources they need to perform their tasks and reduces the risk of credential theft or misuse.
In conclusion, the use of GCP Cross-Project integration instead of Private Key integration offers a more secure and flexible mechanism for granting access to third-party services in GCP. It allows you to implement the principle of least privilege, easily rotate credentials, and provide better auditability and separation of responsibilities.
To learn how to do this, see the GCP Cross Project Integration article.
Important Considerations
When you set up an external cloud storage:
Consider storing your files in a region close to your annotators, for faster file serving. In annotation work, files are streamed from your storage directly to the end user, without having to go through Dataloop servers first, so faster serving can be key for efficient work.
Write access is required, to allow saving thumbnails, modalities, and converted files to a hidden 'dataloop' folder on your storage. A permission "test-file" will be written to your storage when the platform validates permissions.
Annotations and metadata are stored in the Dataloop platform: if you delete a file from your external storage, you'll need to trigger a file delete process in Dataloop, or setup Upstream-sync in advance to ensure these events are covered.
View Your Integrations
Access the Integrations page by clicking on the Integrations from the left-side menu. The page displays the list of Integrations available in your organization.
.png)
Create Cloud Integrations
This integration allows Dataloop to connect to external storage services, such as cloud storage (AWS S3, Google Cloud Storage, Azure Blob Storage) or on-premises systems, for seamless access to datasets and files.
Who can create?
Only users with the Organization Admin or Owner roles are authorized to create integrations.
You can manage and import/export datasets between Dataloop and external storage systems.
This is especially important for handling large volumes of data used in machine learning and AI projects.
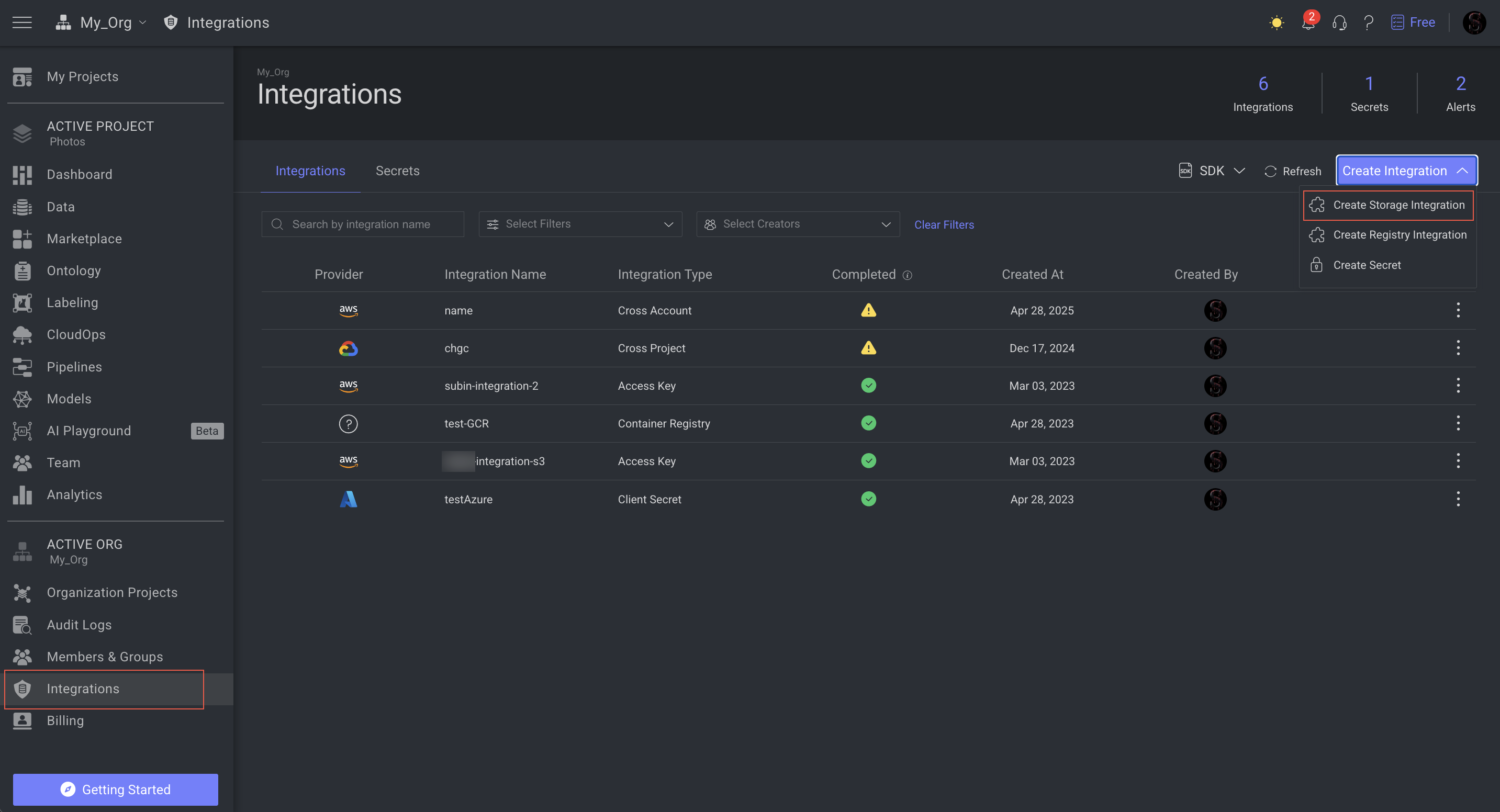
Clicking on the Create Integration -> Create Storage Integration allows you to create the following types of integrations:
AWS
GCP
Azure
Search and Filter Integrations
The following list provides the specific criteria of search and filters for Integrations:
To search: Search Integrations by Integrations Name.
To Filter: Filter the listed integrations by the following criteria:
Provider: The available storage providers for the datasets.
AWS
Azure
GCP
Type: The type of the Integrations.
AWS: Cross Account, STS, and Access Key
GCP: Cross Project, and Private Key
Azure: Client Secret
Untrusted Integrations
Filter integrations based on the email ID of the creator.
List of Integrations
Integrations page displays available Integrations in your organization in a list view. The column values are populated according to the available Integrations.
Column Name | Description |
|---|---|
Provider icon | The icon of the cloud storage provider. |
Integration Name | The name of the integrations. |
Integration Type | The type of the integration depends on the cloud storage provider. |
Completed | It displays whether the necessary steps are completed to establish trust on the Integration. A green-tick mark is displayed if the integration is trusted. If not, a warning icon with a tool-tip explaining the current status is displayed. |
Created At | The creation date of the Integration. |
Created By | The Avatar of the user who created the Integration. You can see the email ID of the user when you hover. |
Click on the More actions (three dots) to view and perform the following actions:
Rename Integration
Edit Integration: When you click, you can modify Access Key integrations' Key and Secret values.
Container Registry integration is editable only from Dataloop SDK.
You cannot edit cross integration.
Copy Integration ID
Delete Integration